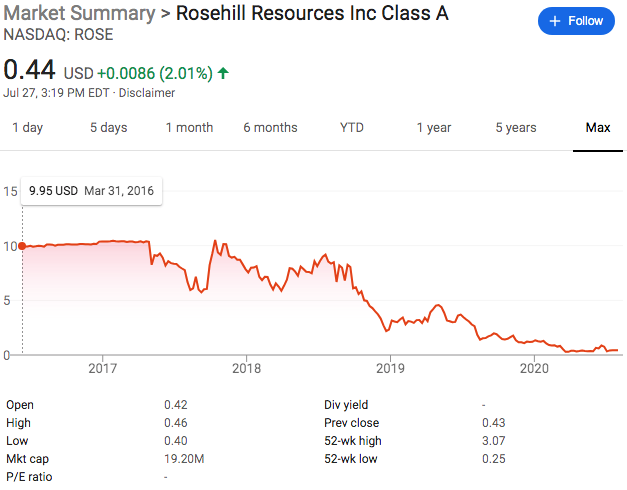
⛽️New Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Filing - Rosehill Resources Inc. ($ROSE)⛽️
Rosehill Resources Inc. ($ROSE)
July 27, 2020
Stop us if you’ve heard this before: Rosehill Resources Inc. ($ROSE), a Texas-based independent E&P company focused, via a fellow-debtor operating company, Rosehill Operating Company LLC (“ROC”), on the Permian Basin (and, more specifically, the Delaware Basin), filed for bankruptcy because of the usual suspects that literally every oil and gas company blames. Seriously, it’s like everyone is just copying and pasting Arya Stark’s hitlist at this point: “Vladimir Putin, Mohammad Bin Salman Al Saud, COVID-19, the competition, too much debt, etc. etc.” Never mind: we’ll stop ourselves. We’ve all heard this before. Many. MANY. Times.
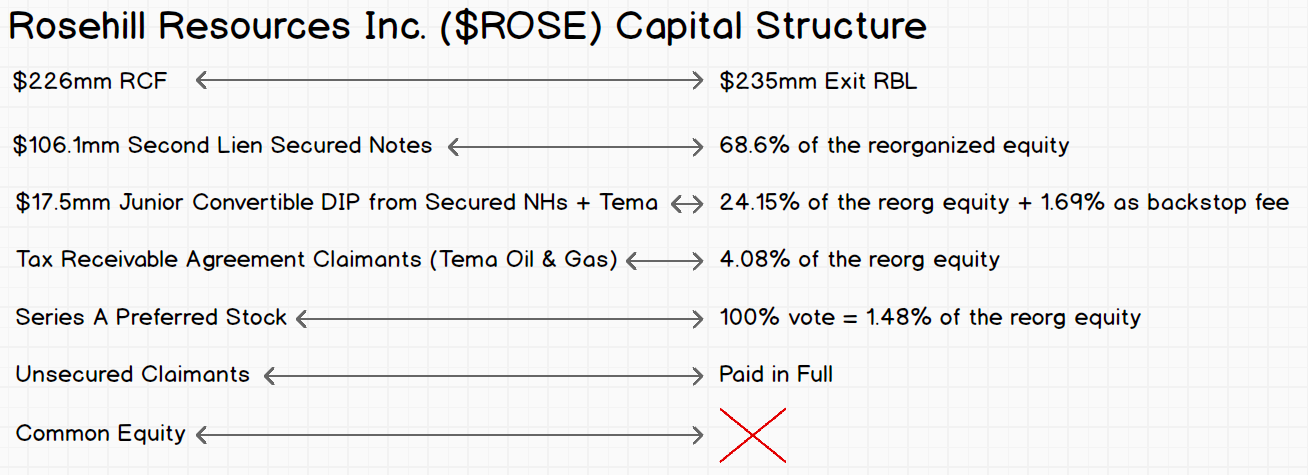
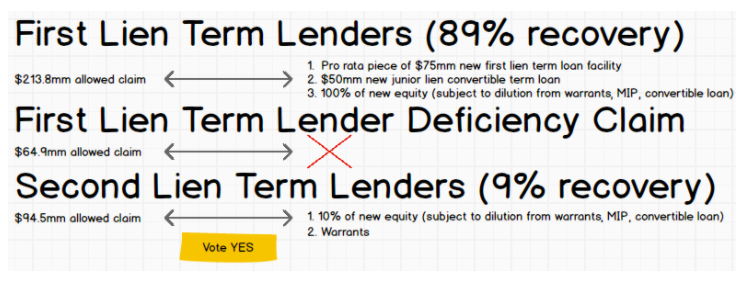
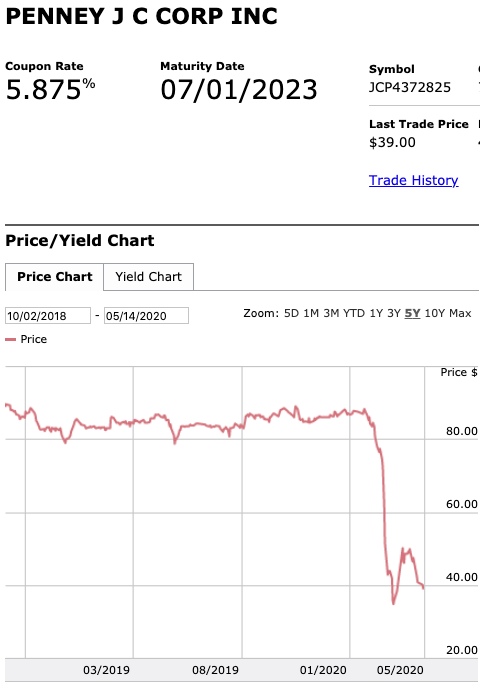
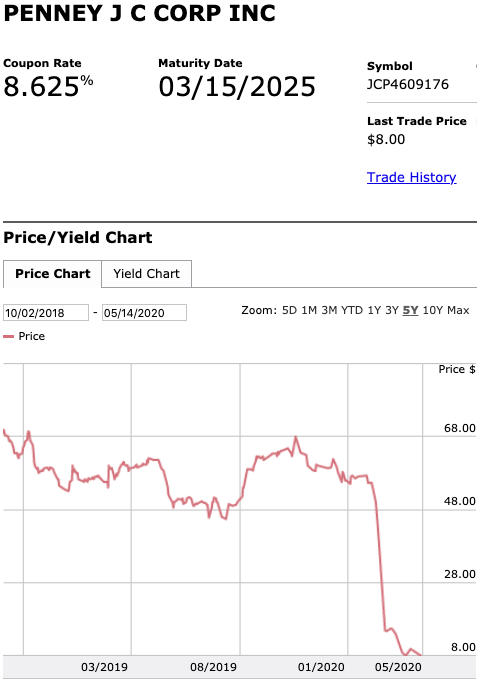
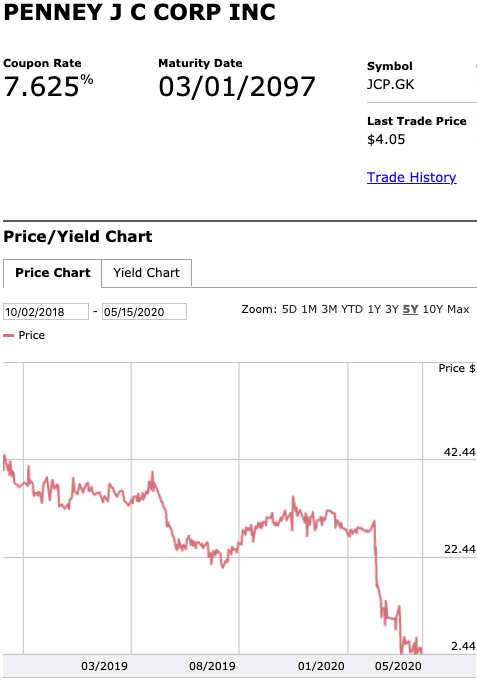
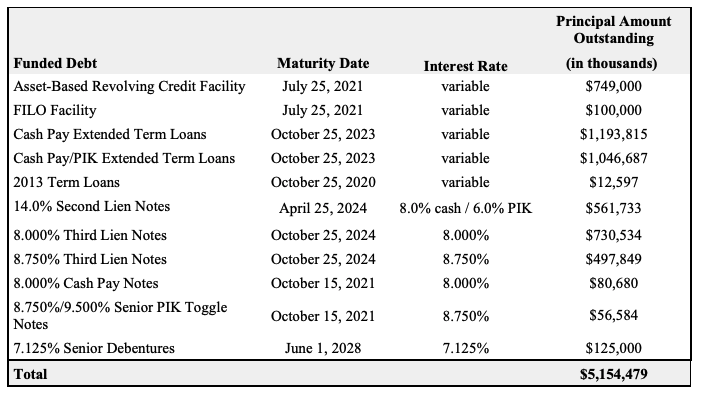
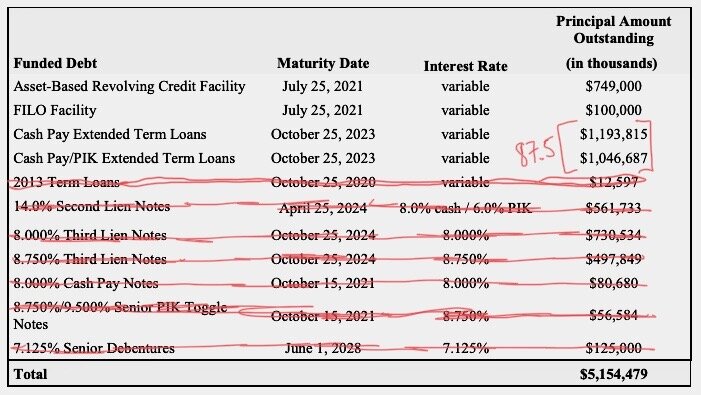
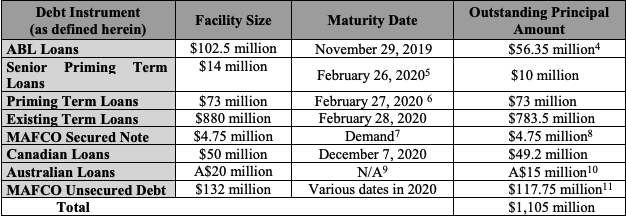
Speaking of the debt, here is what the capital structure looks like and this is what will happen to it pursuant to the prepackaged plan of reorganization that’s already on file:
That should be pretty self-explanatory but there are a few things to highlight:
The $235mm exit RBL actually represents a decreased borrowing base. The original RCF had a maximum commitment of $500mm with a most recent borrowing base of $340mm. That borrowing base amount created a deficiency/liability the company struggled — when coupled with service obligations related to the RCF, secured notes and preferred stock — to make.
The DIP will run at 8% PIK which is better than the 10% cash pay under the secured notes.
In terms of operations, Rosehill operates or owns working interests in 133 oil and gas wells of which 128 are producing or are capable of production. And here’s what that production looks like:
Is that interesting? Not particularly. We include only to demonstrate that we’re not the only ones who are capable of highly unfortunate and irritating typographical errors. More interesting is the fact that Rosehill earned $302.3mm in revenue in ‘19 against $239mm of operating expense. Revenue was basically flat from ‘18 whereas the company’s operating expense increased. On the plus side, the company had some favorable hedge agreements in place which, upon monetization, resulted in $87.6mm in proceeds that the company ultimately used to paydown its RCF immediately prior to the filing. Actually, who are we kidding? That’s not particularly interesting either.
Given how boring this bankruptcy is, the last thing we’ll mention — again because we and the entire world of finance seems to be obsessed with the topic — is that the company emanated out of … wait for it … wait for it … a SPAC!! While the company was originally incorporated in 2015 as a SPAC under the name KLR Energy Acquisition Corporation — sponsored by the KLR Group’s Edward Kovalik, Stephen Lee and Reid Rubinstein — the business corporation that ultimately became Rosehill Resources Inc. occurred in April 2017.
The rest, as they say, is now history. Perhaps we should start taking a running tally: new SPAC IPOs vs. old SPACs that have now filed for chapter 11 bankruptcy!
Jurisdiction: S.D. of Texas (Judge Jones)
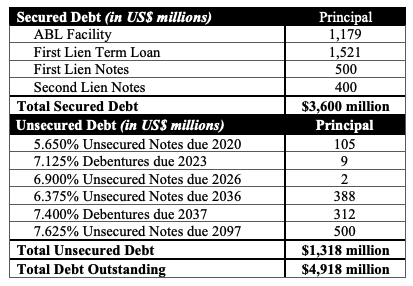
Capital Structure: $226.5mm RCF, $106.1mm second lien secured notes,
Professionals:
Legal: Gibson Dunn & Crutcher LLP (David Feldman, Matthew Kelsey, Dylan Cassidy, Hillary Holmes, Shalla Prichard, Michael Neumeister, Ashtyn Hemendinger) & Haynes and Boone LLP (Kelli Norfleet, Arsalan Muhammad)
Financial Advisor: Opportune LLP
Investment Banker: Jefferies Group LLC (Jeffrey Finger)
Claims Agent: Epiq Corporate Restructuring LLC (*click on the link above for free docket access)
Other Parties in Interest:
Admin Agent: JPMorgan Chase Bank NA
Legal: White & Case LLP (Mark Holmes) & Bracewell LLP (Jason Cohen)
Admin Agent to the Secured Note Purchase Agreement: US Bank NA
Legal: Shipman & Goodwin LLP (Kimberly Cohen, Robert Borden)
Second Lien Noteholders & Series B Preferred Stockholderes & Majority DIP Lenders: EIG Management Company LLC
Legal: Kirkland & Ellis LLP (Chad Husnick, Christopher Koenig, Mary Kogut Brawley) & Zack A. Clement PLLC (Zach Clement)
Tax Receivable Claimant & Preferred and Common Stockholder: Tema Oil & Gas Company
Legal: McDermott Will & Emery LLP (James Kapp III, Brandon White, Nathan Coco, Fred Levenson, Michael Boykins)