New Chapter 11 Bankruptcy Filing - Jason Industries Inc. ($JASN)
Jason Industries Inc.
June 24, 2020
Wisconsin-based Jason Industries Inc. ($JASN) and seven affiliates (the “debtors”) filed a long-anticipated (prepackaged) chapter 11 bankruptcy case in the Southern District of New York on Wednesday — the latest in a line of manufacturers (e.g., Pyxus International Inc., Libbey Glass Inc., Exide Holdings Inc., Pace Industries LLC) to wind its way into bankruptcy court.
The company is an amalgam of decades of growth by acquisition: it launched its components and seating businesses with acquisitions in ‘93 and ‘95, respectively. Everything appeared to be hunky-dory heading into the Great Financial Crisis when things took a turn for the worse.
And so this isn’t the company’s first rodeo in distress. Back in ‘08-’09, the company engaged in a recapitalization transaction supported by Falcon Investment Advisors LLC and Hamilton Lane Advisors; it persevered through the downturn and ultimately sold to a special-purpose-acquisition-company (Quinpairo Acquisition Corp.) in 2014 for $538.6mm. The acquisition was financed through a combination of (i) the $172.5mm raised by the SPAC in its ‘13 IPO, (ii) rollover equity from the aforementioned sponsors (and management), and (iii) $420mm of first and second lien debt. Stick a pin in that last number: it comes back to haunt the debtors. 👻
In the years since, the company streamlined its operations — selling off assets (i.e., its fiber solutions business and a metal components business) and consolidating around two primary business segments. Through their industrial segment, the debtors manufacture a bunch of stuff used for industrial and infrastructure applications; and through their engineered components segment, the debtors manufacture (a) motorcycle seats, (b) operator seats for construction, agriculture, law and turf care and other industrial equipment markets, and (c) seating for the power sports market. Said another way, the company is heavily indexed to the automotive, heavy truck, steel and construction markets. Powered by approximately 700 employees in the US, the company did $338mm in net sales in 2019.
And that is part of the problem. $338mm in net sales represented an 8.2% ($30.1mm) dropoff from 2018. Adjusted EBITDA declined from $36.7mm in ‘18 to $24.8mm in ‘19. Both segments have been underperforming for years. The question is why?
The debtors cite a dramatic dropoff in demand in ‘19. They note:
This reduction was largely caused by reduced end market demand in key industries across the portfolio, specifically, weak economic conditions in Europe and Asia, lower industrial production in North America, and softening end market demand from OEM customers. For example, since as early as the first quarter of 2019, the Company has experienced reduced OEM build and channel inventory destocking. These problems were exacerbated by the operational disruption and demand reduction caused by the COVID-19 pandemic.
Consequently, the debtors busted out the standard playbook to try and manage liquidity (while parallel-tracking a fruitless pre-petition sale and marketing effort). They (a) intensified focus on growing market segments, (b) reduced capital investment in non-core businesses, (c) cut/furloughed labor and instituted pay reductions for execs and other employees (and eliminated a 401(k) match program), (d) closed plants and manufacturing facilities and deferred rent payments or negotiated reduced rent at leased properties, (e) accelerated the consolidation of plants acquired in a recent acquisition, and (f) invested in automation at their facilities to reduce future operating costs (read: replace expensive human beings) and expand margins. Still, the debtors struggled.
…the pandemic’s impact on orders and revenues, combined with preexisting fixed costs and debt service requirements, have constrained available working capital, reduced profitability and cash flow, and significantly impaired the Company’s ability to adequately finance operations.
Which gets us back to the capital structure:
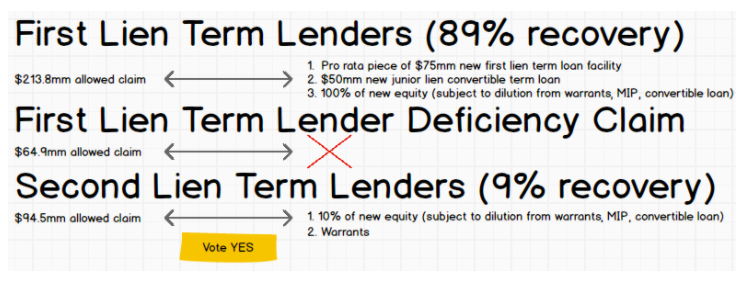
Given where EBITDA numbers were coming in, this thing’s leverage ratio was through the roof. More to the point, the debtors deferred a March 31 second lien interest payment and had been operating under a series of forbearance agreements ever since. Luckily, the capital structure isn’t all-too-complicated and lends itself well to a prepackaged bankruptcy. And so here we are with a restructuring support agreement and proposed prepackaged plan which will effectively turn the company over to the first lien term lenders and, but for some warrants, wipe out the second lien term lenders. Here’s how the above capital structure breaks down:
Source: PETITION LLC
A couple of notable features here:
Drop it Likes its Hot. There’s a “first lien put option” baked into the plan pursuant to which any first lien term lender who doesn’t want to own equity or the junior converts can “put” its pro rata share of that equity/converts to a first lien lender, Pelican Loan Advisors III LLC (or lenders as the case may be), which has agreed to backstop this baby. Pelican is managed by Monomoy Capital Partners.
F*ck You Pay Me. Those first lien lenders who consented to forbearances all of those months are about to get paaaaaaayyyyyyyyydd. They’ll receive a pro rated share of and interest in $10mm worth of open market purchases by the debtors of first lien credit agreement claims held by consenting first lien lenders AND a forbearance fee equal to 4.00% of the principal amount of the first lien credit agreement loans held by the consenting lenders as of a date certain. The open market purchases were, presumably, accomplished prior to the filing with 2% of the fee already paid and the remaining 2% to be paid-in-kind on the earlier of the termination date of the RSA or the plan effective date.
It’s a Trap! Warrants are technically going to be issued to the first lien term lenders and “gifted” to the second lien lenders. But only if they vote to accept the plan. Given the midpoint total enterprise value of $200mm and resultant deficiency claim, this is a nice absolute priority rule workaround. As reflected in the graphic above, the allowed deficiency claim of $64.9mm is obviously impaired and will get a big fat 🍩.
And so this is what the capital structure will look upon emergence:
The first lien lenders have consented to the use of their cash collateral to fund the cases.*
* ⚡️July 15, 2020 Update: The Second Lien Ad Hoc Committee, however, filed a limited objection to the cash collateral motion on the basis that a final order should (a) limit any credit bid to their collateral (noting that a material amount of assets — including 35% of the equity in foreign subs — are excluded from the first lien lenders’ collateral package, and (b) require a finding that there’s diminution of value of the first lien lenders’ collateral such that they, despite providing no new financing, ought to be granted a superpriority lien on previously unencumbered assets. The Committee also previewed objections it will have to the plan of reorganization. For a purportedly “prepackaged” chapter 11, this one looks like it could be more contentious than most. A final hearing on the cash collateral motion is set for July 22, 2020.⚡️
Jurisdiction: S.D. of New York (Judge Drain)
Capital Structure: see above.
Company Professionals:
Legal: Kirkland & Ellis LLP (Jonathan Henes, Emily Geier, Laura Krucks, Dan Latona, Jake Gordon, Yates French)
Financial Advisor: AlixPartners LLP (Rebecca Roof)
Investment Banker: Moelis & Company LLC (Zul Jamal)
Claims Agent: Epiq Bankruptcy Solutions LLC
Other Parties in Interest:
Large equityholder: Wynnefield Capital Management LLC
Ad Hoc Group of First Lien Creditors (Credit Suisse Asset Management LLC, Voya CLO Ltd., American Money Management Corp., First Eagle Alternative Credit LLC, Angel Island Capital Services LLC, Monomoy Capital Partners LP, Z Capital Partners LLC)
Legal: Weil Gotshal & Manges LLP (Matthew Barr, Ryan Preston Dahl, Alexander Welch)
Financial Advisor: Houlihan Lokey Capital Inc.
First Lien Agent: The Bank of New York Mellon
Second Lien Agent: Wilmington Savings Fund Society FSB
Legal: Seward & Kissel LLP (John Ashmead, Gregg Bateman)
Ad Hoc Group of Second Lien Lenders: Corre Partners Management LLC, Newport Global Advisors
Legal: Brown Rudnick LLP (Steve Pohl, Shari Dwoskin, Kenneth Aulet)
Financial Advisor: DC Advisory LLC
Update July 17, 2020