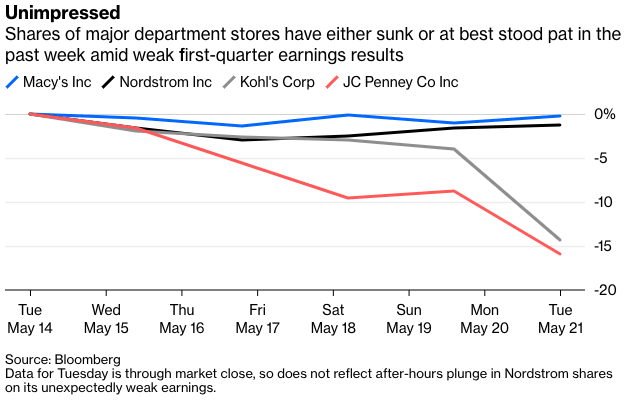
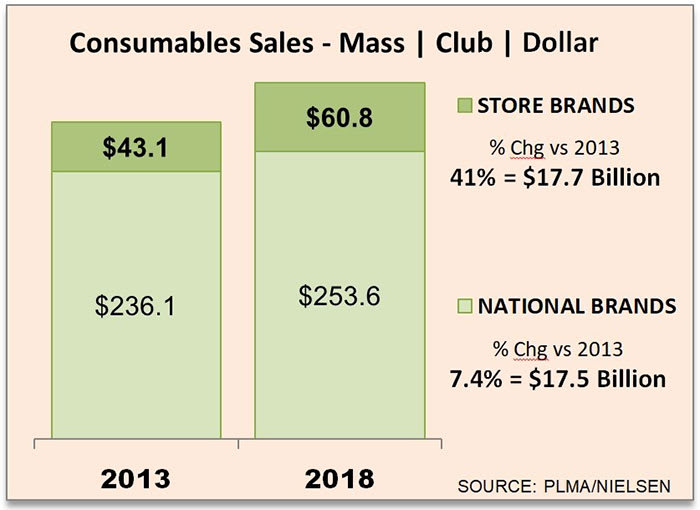
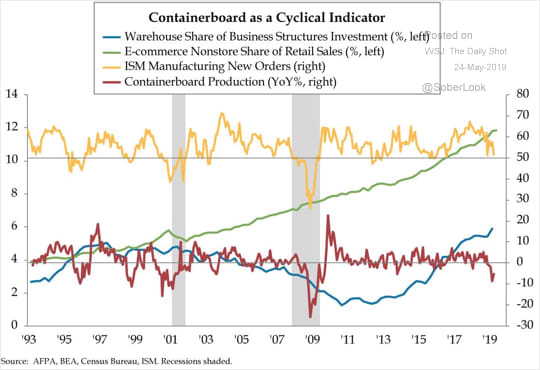
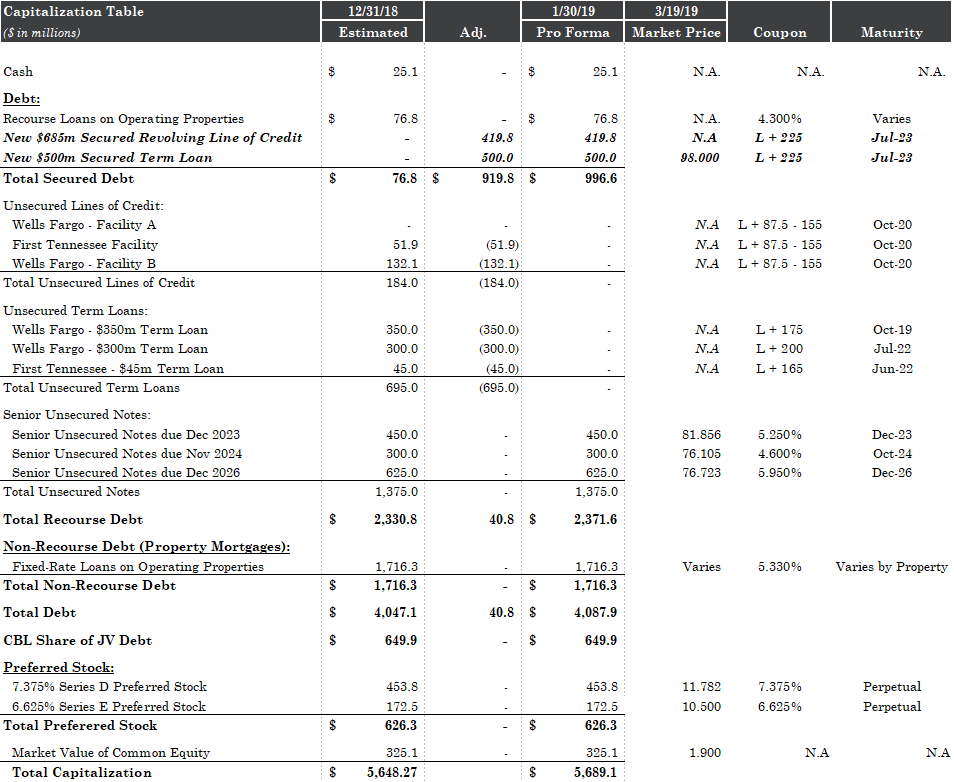
2019 has already been a rough year for retail. Beauty Brands LLC, a Kansas City-based brick-and-mortar retailer with 58 stores in 12 states filed for chapter 11 bankruptcy in the first week of January. Then, last week, both Shopko (367 stores) and Gymboree (~900 stores) filed for chapter 11 bankruptcy — the former hoping to avoid a full liquidation and the latter giving up hope and heading straight into liquidation (it blew its first chance in bankruptcy). And, of course, there’s still Charlotte Russe, Things Remembered, Payless and others to keep an eye on.
All of this has everyone on high alert. Take this piece from The Wall Street Journal. Pertaining to J.C. Penney ($JCP) and Sears Holding Corporation ($SHLDQ), the WSJ notes:
J.C. Penney Co.’s sales are falling, its stores are stuck in malls and the turnaround strategy keeps changing. Now, three months after the embattled retailer hired a new chief executive, a handful of senior positions remain vacant.
The series of events is prompting analysts and other industry experts to question whether Penney can avoid the fate of fellow department-store operator Sears Holdings Corp., which filed for bankruptcy and barely staved off liquidation.
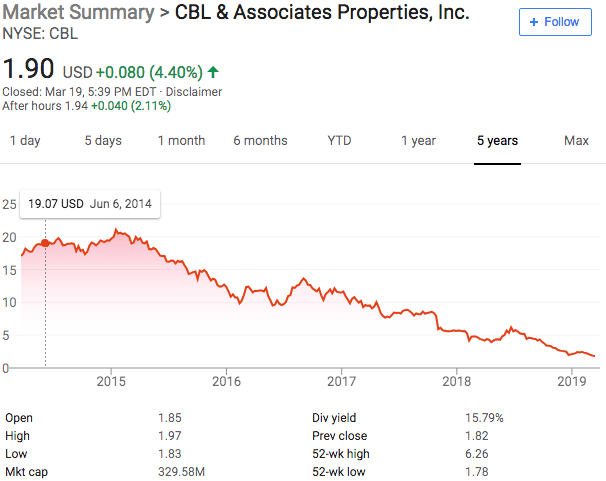
The Plano, Texas-based chain was once the go-to apparel retailer for middle-class families. It and Sears had once dominated American retailing but lost their customers, first to discounters like Walmart , then to fast-fashion retailers and off-price chains like T.J. Maxx. The shift to online shopping hastened their decline.
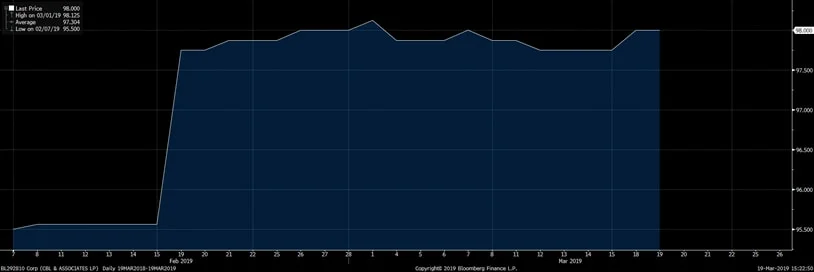
First, the Sears Holding Corporation ($SHLDQ) drama continues as the company heads towards a contested sale hearing in the beginning of February. To say that it “staved off liquidation” is, at this juncture, factually incorrect. While the company’s prospects have improved along with Mr. Lampert’s purchase offer, it is not a certainty that the company will be able to avoid liquidation. At least not until the Official Committee of Unsecured Creditors’ objection is overruled and the bankruptcy court judge blesses the Lampert deal. The sale hearing is slated for February 4.
Second, we were relieved to FINALLY see an article about retail that didn’t pin the blame solely at the feet of Amazon Inc. ($AMZN). As we’ve been arguing since our inception, the narrative is far more nuanced than just the “Amazon Effect.” To point, Vitaliy Katsenelson recently wrote in Barron’s:
Retail stocks have been annihilated recently, even though retail sales finished 2018 strong. The fundamentals of the retail business look horrible: Sales are stagnating, and profitability is getting worse with every passing quarter.
Jeff Bezos and Amazon.com get most of the blame, but this is only part of the story. Today, online sales represent only 8.5% of total retail sales. Amazon, at about $100 billion in sales, accounts only for 1.6% of total U.S. retail sales, which at the end of 2018 were around $6 trillion. In truth, the confluence of a half-dozen unrelated developments is responsible for weak retail sales.
He goes on to cite a shift in consumer spending to more expensive phones, more expensive phone bills, more expensive student loan bills and more expensive health care costs as contributors to retail’s general malaise (PETITION Note: yes, it appears that lots of things are getting more expensive. Don’t tell the FED.). More money spent there means less discretionary income for the likes of J.C. Penney. Likewise, he highlights the change in consumer habits. He writes:
We may not care about clothes as much as we may have 10 or 20 years ago. After all, our high-tech billionaires wear hoodies and flip-flops to work. Lack of fashion sense did not hinder their success, so why should the rest of us care about the dress code?
And:
Consumer habits have slowly changed, including the advent of rental clothes from companies like Rent the Runway and LeTote.
We’ve previously written extensively about the rental and resale wave. We wrote:
Indeed, per ThredUp, a second-hand apparel website, the resale market is on pace to reach $41 billion by 2022 and 49% of that is in apparel. Moreover, resale is growing 24x more than overall apparel retail. “[O]ne in three women shopped secondhand last year.” 40% of 18-24 year olds shopped retail in 2017. Those stats are bananas. This comment is illustrative of the transformation taking hold today,
“The modern consumer now has a choice between shopping traditional retail or trying new, innovative business models. New apparel experiences and brands are emerging at record rates to replace old ones. Rental, subscription, resale, direct-to-consumer, and more. The closet of the future is going to look very different from the closet of today. When you get that perfectly curated assortment from Stitch Fix, or subscribe to Rent the Runway’s everyday service, or find that killer handbag on thredUP you never could have afforded new, you start realizing how much your preferences and behavior is changing.”
Lots of good charts here to bolster the point.
That wave just got a significant shot of steroids.
Earlier this month Netflix Inc. ($NFLX) debuted “Tidying Up with Marie Kondo,” a show that springs off of Ms. Kondo’s hit 2014 book, “The Life-Changing Magic of Tidying Up: The Japanese Art of Decluttering and Organizing.” The news since is not too encouraging for retailers.
Per NPR, “Thrift Stores Say They’re Swamped With Donations After ‘Tidying Up with Marie Kondo’” (audio and audio transcript). Indeed, thrift stores like Goodwill are seeing an uptick in donations across the country (and Canada). The Wall Street Journal published a full feature predicated upon “throw a lot of sh*t out.”
Of course, all of this decluttering is an opportunity. Anna Silman writes in The Cut:
Well, congrats to all the people who have committed to the KonMari life and ridded themselves of the burden of their unwanted possessions, and who now have to waste 15 minutes a day folding their underwear into tiny rectangles. But also, good for us! Imagine how many bad choices people are liable to make in a feverish post New Year’s Kondo-inspired purge? Mistakes will be made. Purgers are going to see that lavish fur cape they never wore and deem it impractical; come Game of Thrones finale cosplay time, they’re going to rue their hastiness. Conscientious closet cleaners will dispose of the low-rise jeans they haven’t worn since the mid-aughts, but the joke’s on them, because low-rise jeans are coming back, bitches!
So, my fellow anti-Kondoers, if you’re in a post-holiday shopping mood, get thee to thy nearest second-hand clothing store Beacon’s (or Goodwill, or Buffalo Exchange, or Crossroads, or the internet) and get started on building your 2019 wardrobe. And if you arrive at your nearest resale outlet and see a long line, don’t worry: Those people are there to sell. Those aren’t your people. Forget them. Focus on the racks — those sweet, newly stocked, overflowing racks, where so much joy awaits.
It’s just like the old adage: One woman’s trash is another woman’s treasure, especially because most of it was never trash to begin with.
Likewise, Lia Beck writes in Bustle, “…get out there and find some things that spark joy for you.”
And reseller The RealReal is signaling that resale is so big that it’s ready to IPO. Talk about opportunistic. No better time to do this than during Kondo-mania. The company has raised $115mm in venture capital from Perella Weinberg Partners, Sandbridge Capital and Great Hill Partners, most recently at a $745mm valuation.
None of this is a positive for the likes of J.C. Penney. They need consumers to consume and clutter. Not declutter. Not go resale shopping. We can’t wait to see who is first to mention Marie Kondo as a headwind in a quarterly earnings report. Similarly, we wonder how long until we see a Marie Kondo mention in a chapter 11 “First Day Declaration.” 🤔