If you’re Steve Rogers, Encino Man, or were otherwise frozen somehow from 2014 through 2017 and missed the oil and gas downturn, Bethany McLean’s “Saudi America” will give you a nice high-level overview of American oil policy and fracking. It discusses Aubrey McClendon, the Obama-era change oil export policy, President Trump’s notion of energy independence, the rise of the West Texas’ Permian basin and more. She writes:
“What people still fail to understand is that the most cyclical number we have is the theoretical break-even,” one oil man says. “There will be stories about how the $40 break-even became the $70 break-even, and people will say ‘Who lied to me?’”
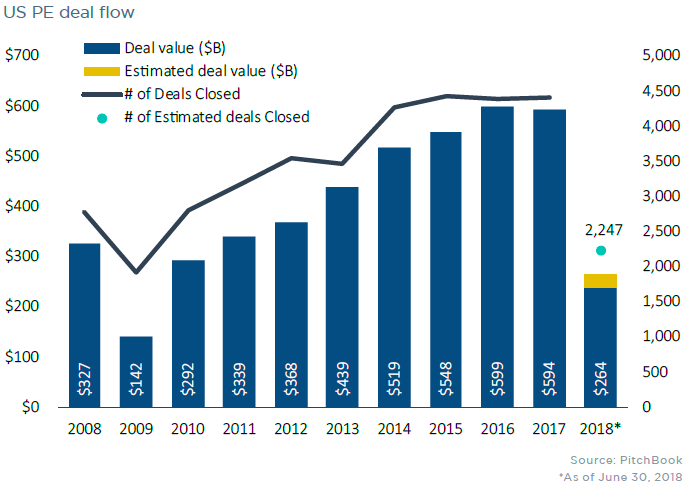
And so it is that the most important factor in the comeback of shale is the same thing that started the boom in the first place: The availability of capital. “It came back because Wall Street was there,” says longtime short-seller Jim Chanos. In 2017, U.S. frackers raised $60 billion in debt, up almost 30 percent since 2016, according to Dealogic.
Wall Street’s willingness to fund money-losing shale operators is, in turn, a reflection of ultra-low interest rates. That poses a twofold risk to shale companies. In his paper for Columbia’s Center of Global Energy Policy, Amir Azar noted that if interest rates rose, it would wipe out a significant portion of the improvement in break-even costs.
But low interest rates haven’t just meant lower borrowing costs for debt-laden companies. The lack of return elsewhere also let pension funds, which need to be able to pay retirees, to invest massive amounts of money with hedge funds that invest in high yield debt, like that of energy firms, and with private equity firms — which, in turn, shoveled money into shale companies, because in a world devoid of growth, shale at least was growing. Which explains why Lambert, portfolio manager of Nassau Re, says “Pension funds were enablers of the U.S. energy revolution.”
Ah, yield baby yield.
A lot of the U.S. energy revolution and recovery from ‘14-’17 is coming from the West Texas’ Permian basin. McLean writes:
In 2010, the Permian Basin was producing just shy of 1 million barrels a day. In 2017, that had more than doubled to over 2.5 million barrels a day. By August, output from the Permian alone exceeded that of 8 of the 13 members of OPEC, according to Bloomberg. The International Energy Agency predicts that output will hit more than 4 million barrels a day within a few years. Production from the Permian is the primary driver behind skyrocketing estimates of how much oil the U.S. will produce.
Apropos, Bloomberg noted this week:
To get a toehold in the prolific Permian Basin, private equity is increasingly betting on a relatively obscure, and potentially risky, part of the pipeline industry.
Operations in the Permian that gather oil and gas, and process fuel into propane and other liquids, have drawn almost $14 billion in investment since the start of 2017, with $9.2 billion of that coming from private companies, according to Matthew Phillips, an analyst at Guggenheim Securities LLC.
Specifically, Bloomberg is referring to midstream companies manufacturing gathering and processing pipeline assets that transport oil and gas across states. Producers commit to pay for space in the pipes over a period of years. Restructuring professionals are very familiar with these gathering contracts: they were the subject of many a dispute during the recent downturn.
…investors in gathering pipes and processing plants are forced to lean on long-term projections, since their projects depend on continuous output over time from the same area.
“Any time there’s massive supply growth, there is some risk-seeking behavior,” said Jeff Jorgensen, portfolio manager and director of research at Brookfield Asset Management Inc.’s Public Securities Group. There’s a tendency by some to “invest in production profiles that are, let’s just say, hilariously aggressive in their assumptions” for the future, he said.
It’s easy to see where that aggressiveness is coming from. Researcher IHS Markit predicts output in the Permian Basin will double by 2023 to reach 5.4 million barrels a day. That’s more than every OPEC country except Saudi Arabia. By 2035, it could hit 6.3 million barrels, according to Wood Mackenzie.
Bloomberg continues:
…with the surge of private equity money giving way to smaller players that may be taking on added debt to pay for pricey projects, the risk increases dramatically.
“There’s definitely some sloppiness in the gathering and processing space,” she said. “The cash flow isn’t going to be what they expected, so we could see some of the smaller players financially weaken, and that may lead to consolidation.”
With oil prices on the rise, however, the risk may seem worth taking. Memories are short. And confidence in break-even costs must be through the roof. Regardless of whether President Trump is happy with oil prices where they are.
The bottom line is that in this oil and gas recovery, there are clear winners and losers. The Permian is a big winner. This explains the recent S-1 filing of Riley Exploration — Permian LLC ($REPX)(owned by Yorktown Partners LLC, Bluescape Energy Partners LLC and Boomer Petroleum LLC), which has 65k+ net acres in the Permian as of June 30, 2018. Look at that name: they’re clearly sending a message that screams “pureplay Permian exploration and development company.” It’s like companies putting “.com” in their name during the dot.com bubble and “blockchain” in their name in the more recent crypto bubble. Smart move.
The Bakken in North Dakota appears to be back too. Per Bloomberg:
North Dakota’s oil production surged to a new record in July, putting the mid-western state on par with OPEC member Venezuela.
Home to the Bakken shale play, North Dakota pumped 1.27 million barrels a day in July, according to state figures released Friday. That’s roughly the same output as Venezuela during the month. The South American nation, whose oil industry has collapsed amid a prolonged financial crisis, saw production fall further in August to 1.24 million barrels a day -- about half the level seen in early 2016, according to data from OPEC secondary sources.
Where are the losers? Look at the Anadarko/Woodford area (read: West Oklahoma). In quite the juxtaposition to Riley Exploration, this week Tapstone Energy, a Blackstone-backed oil and gas exploration and production company withdrew its proposed $400mm IPO. Those closely watching Gastar Exploration Inc. ($GSTC) will find it located there too. The stock was delisted, trades over-the-counter at $0.06/share. The bankruptcy clock is ticking.
Like we said. Winners and losers.