🛋There's Disruption Afoot in the Furniture Space🛋
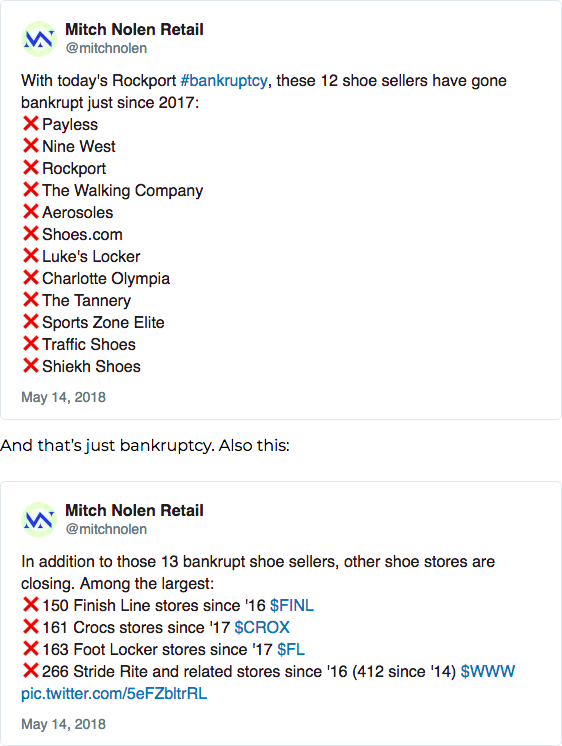
Add Furniture to the List of Disrupted Categories (Home Heritage Group Inc. Filed for Bankruptcy)
“New Chapter 11 Filing!” Or is it technically a Chapter 22? 🤔
We know what you’re thinking. You’re thinking “this filed a few days ago and I’ve already read all about it.” You may have read something about it, but not like this. Bear with us…
Home Heritage Group Inc. (“HHG”) is a North Carolina-based designer and manufacturer of home furnishings; it sells product via (i) retail stores, (ii) interior design partners, (iii) multi-line/independent retailers, and (iv) mass merchant stores.” In addition, the company has an international wholesale business.
Why do we mention Chapter 22? For the uninitiated, Chapter 22 in bankruptcy doesn’t actually exist. It is a somewhat snarky term to describe companies that have round-tripped back into chapter 11 after a previous stint in bankruptcy court. That, to some degree, is the case here.
WAAAAAAAY back in November 2013, KPS Capital Partners LP formed the newly bankrupt HHG entity to acquire a brand portfolio and related assets out of the bankruptcy estate of Furniture Brands International Inc. (“FBI”). FBI had been, in the early 2000s, a very successful purveyor of various furniture brands — to the tune of $2b in annual sales. But in the 12 months prior to the acquisition, the company’s sales were down to $940mm and, more importantly, its EBITDA was negative $58mm. At the time of filing, it had $142mm in total funded debt outstanding, $200mm in unfunded pension obligations and another $100mm in general trade obligations.
Given this debt, a decline in sales at the time was devastating. The company noted in its court filings on September 9, 2013 (Docket #16):
As a manufacturer and retail of home furnishings, Furniture Brands’ operations and performance depend significantly on economic conditions, particularly in the United States, and their impact on levels of existing home sales, new home construction, and consumer discretionary spending. Economic conditions deteriorated significantly in the United States and worldwide in recent years as part of a global financial crisis. Although the general economy has begun to recover, sales of residential furniture remain depressed due to wavering consumer confidence and several, ongoing global economic factors that have negatively impacted consumers’ discretionary spending. These ongoing factors include lower home values, prolonged foreclosure activity throughout the country, a weak market for home sales, continued high levels of unemployment, and reduced access to consumer credit. These conditions have resulted in a decline in Furniture Brands’ sales, earnings and liquidity.
Sales have continued to be depressed as a result of a sluggish recovery in the U.S. economy, continuing high unemployment, depressed housing prices, tight consumer lending practices, the reluctance of some households to use available credit for big ticket purchases including furniture, and continuing volatility in the retail market.
PETITION Note: My, how things have changed. Just reflect on that synopsis of the economy a mere five years ago. The company also noted that:
…some of the Company’s larger brands have lost some of their market share primarily due to competition from suppliers who are able to produce similar products at lower costs. The residential furniture industry is highly competitive and fragmented. Furniture Brands competes with many other manufacturers and retailers, some of which offer widely advertised, well-known, branded products, and other competitors are large retail furniture dealers who offer their own store-branded products.
All of these factors stormed together to constrain the company’s liquidity and force a chapter 11 filing and eventual sale. KPS purchased several of the FBI brands for $280mm (subject to working capital adjustments), including Thomasville, Broyhill, Lane, Drexel Heritage, Henredon, Pearson, Hickory Chair, Lane Venture, and Maitland-Smith. In other words: brands that your grandfather would know and you would shrug at the mere mention of. Well, some of you anyway.
Fast forward five years and the successor entity HHG has $280mm of debt and…you guessed it…severe liquidity constraints. In its first day filing papers, HHG notes that the previous bankruptcy continues to have lasting effects on its business; it highlights:
Following years of sales declines, many furniture retailers had lost faith in the ability of the Company to produce, deliver, and service its products, and the bankruptcy led many of them to shift their purchases to a variety of competitors or even further utilize their own private label offerings.
This is what people still nostalgically refer to as “bankruptcy stigma.” Indeed, it still exists. The company continued:
In addition, the Company’s operations and performance depend significantly on economic conditions, particularly in the United States, and their impact on levels of existing home sales, new home construction, and consumer discretionary spending. Although economic conditions have been steadily improving in recent years, the Debtors have struggled to adjust to certain shifts in consumer lifestyles, which include: (i) lower home-ownership levels and more people renting; (ii) more apartment living and single-person households; (iii) older consumers that want to age in place; and (iv) cash-strapped millennials that are slow in forming households relative to prior generations.
Haha! The poor millennials. Apparently an entire generation is “cash-strapped” and prefers to sleep in a tent under their WeWork desks. Blame the avocado toast and turmeric lattes. But, wait, there’s more:
Consumer browsing and buying practices are rapidly shifting as well toward greater use of social media, internet- and app-based catalogs and e-commerce platforms, and the Company has been unable to develop a substantial sales base for its brands through this key growth channel.
Furthermore, the residential furniture industry is highly competitive and fragmented. The Company competes with many other manufacturers and retailers, some of which offer widely advertised, well-known, branded products, and other competitors are large retail furniture dealers who offer their own private label products. This competitive landscape has proved challenging for some of the Company’s larger brands as well-capitalized competitors continue to gain market share at the expense of the Debtors. (emphasis added)
PETITION Note: My, how things have remained the same. Sound familiar? Have to hand it to the professionals here: why reinvent the wheel when you can just crib from the prior filing? We guess being a repeat customer in bankruptcy has its benefits!! Chapter 22!!!
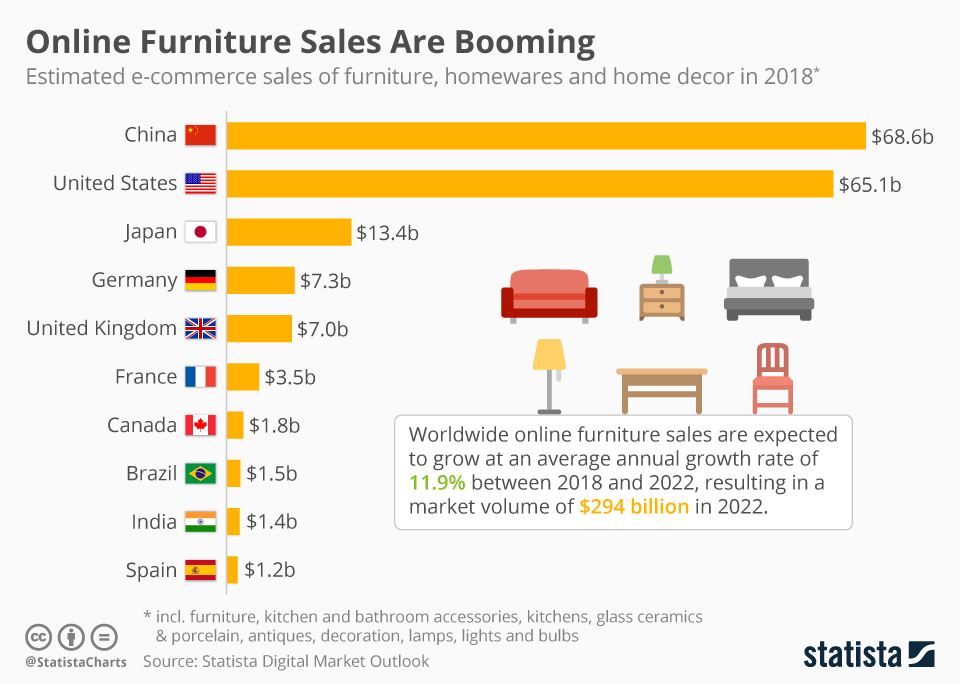
<p>Meanwhile a short digression relevant to those last two quoted paragraphs. According to Statista, worldwide online furniture and homewares sales are expected to be close to $190 billion. Take a look at this chart:
RetailDive notes:
E-commerce furniture sales have emerged as a major growth area, rising 18% in 2015, second only to grocery, according to research from Barclays.
Accordingly, GartnerL2 cautions that:
…home brands now have an outsized onus to produce best-in-class product pages for the influx of online shoppers. However, many brands have failed to deliver and aren’t keeping pace with industry disruptors.
Sounds like HHG has, admittedly, fallen into this category.
GartnerL2 highlights the disparate user experiences offered by Williams-Sonoma-owned West Elm and Chicago-based DTC disruptor Interior Define, which was founded in 2013 and has raised $27mm in funding (most recently a Series B in March). The latter offers extensive imagery, a visual guide and an augmented reality mobile app. All of these things appeal to the more-tech-savvy (non-cash-strapped??) millennial buyer.
And that is precisely the demographic that La-Z-Boy Incorporated ($LZB) is going after with its purchase of Joybird, a California-based direct-to-consumer e-commerce retailer and manufacturer of upholstered furniture. Founded in 2014, its $55mm in reported revenue last year took a chunk out of, well, someone. Other players in that space include Burrow ($19.2mm in total funding; most recent Series A in March from New Enterprise Associates) and, of course, Amazon’s in-house furniture brands, Rivet and Stone & Beam. <p><end>
All of these factors resulted in continual YOY declines in sales and a liquidity squeeze. Now, therefore, the company is in bankruptcy to effectuate a sale — or sales — of its brands to prospective bidders. It has one purchaser in line for the “Luxury Group” and, according to the court filing, appears close to an agreement with a stalking horse buyer of the Broyhill and Thomasville & Co. properties. In the meantime, the company has a commitment from prepetition lender PNC Bank NA for a $98mm DIP, of which $25mm Judge Gross granted on an interim basis.