When Will ICOs Become a Thing in Distress? (Short SEC Regulations)
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
On Valentine’s Day, in “Misplaced Optimism in Retail: L Brands - What the Holy F*#*?,” we clowned on Leslie Wexner’s aggressive approach to retail and said “tell us that you don’t want to short the sh*t out of the stock.” It was trading at $49.87/share. Now...
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
We have spoken a lot about direct-to-consumer digitally native brands having a tremendous — and understated (in restructuring circles) — affect on brick-and-mortar retail. Apparel in particular. PETITION readers are already familiar with Wish, a unicorn shopping platform with a valuation north of $8 billion. It’s secret sauce is allowing consumers to purchase clothes directly from Chinese factories. Imagine all of the middlemen cut out of that equation. No “brand tax” either.
Earlier this week Sequoia Capital China led an investment in Jollychic, a China-based e-commerce startup that lets Middle Eastern shoppers order unbranded products from Chinese factories.
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
Back in October, we asked “Is Another Wave of Auto-Related Bankruptcy Around the Corner?” The (free) piece is worth revisiting — particularly in light of Tesla’s recent travails. Among many other things, we wrote:
Supply Chain Distress. Last year we saw DACCO Transmission Parts Inc. file for bankruptcy. During the Summer, Takata Inc. filed for bankruptcy (on account of a massive liability, but still) and Jack Cooper Enterprises Inc., a finished-vehicle logistics/transportation provider, reached a consensual agreement with its noteholders that kept the company out of bankruptcy court. For now. Then, a little over a week ago, GST Autoleather Inc. filed for bankruptcy, citing declining auto output. Is this the canary in the coal mine? Hard to say. Literally on the same day that GST filed for bankruptcy - again, citing declining auto output - General Motors, Ford and other OEMs reported the first YOY sales increase (10%), surprising to the upside. It seems, however, that the (sales) uptick may be artificial: in part, it's attributable to (a) Hurricane Harvey damage and mass vehicle replacement; and (b) heavy vehicle discounting. On a less positive note, Ford announced that it will be slashing billions in costs to shore up its financial condition; it also announced back in September that it would slash production at five of its plants. And General Motors Co. announced earlier this week that it would be idling a Detroit factory and cutting production. Production levels, generally, are projected to decline through 2021. Obviously, reduced production levels and idled plants portend poorly for a lot of players in the auto supply chain.
But, with limited exception (like Nissan’s announcement this week that it would cut U.S. production by 20%), the auto world has been largely quiet since then. Another exception: International Automotive Components Group S.A., a Detroit-based interior parts manufacturer with 77 manufacturing plants worldwide, announced, in April, a new financing transaction through the issuance of $215 million of ‘23 second lien notes funded by Gamut Capital Management LP. Perhaps we just need to be more patient?
Rumblings abound around two more names that may be in more near-term trouble. First, American Tire Distributors’ suffered downgrades on the heels of the announcement that Goodyear Tire & Rubber Co. ($GT) opted to discontinue use of ATD as a distributor. Notably, GT’s stock, itself, is down 20% in the last year:

Anyway, back to ATD. Per Crain’s Cleveland Business,
The news cratered the market value of ATD's $975 million of bonds and its $700 million term loan. S&P Global Ratings quickly cut the company's credit grade deeper into junk and Moody's followed suit, saying its capital structure was no longer sustainable.
Then, on May 9, the 800-pound gorilla entered the industry, as Amazon.com Inc. teamed up with Sears Holdings Corp. to allow customers to buy replacement tires online and have them installed at the troubled department store.
The moves signal radical changes in the replacement-tire market. Manufacturers are taking control of their own distribution, cutting out wholesalers like ATD, and along with retailers are developing their own internet capabilities to reach consumers directly, according to New York-based research firm CreditSights.
Ah, there it is: Amazon ($AMZN). Is a PETITION entry complete without the mandatory Amazon reference? Indeed, Moody’s noted,
“All else being equal, the magnitude of the associated earnings and cash flow decline will compound an already levered financial risk profile, rendering a pre-emptive debt restructuring increasingly likely, in our estimation.”
The Huntersville North Carolina company is a wholesale distributor of tires, custom wheels and other related auto equipment; it is a behemoth with $5.3 billion in revenues in 2017 and 140 distribution centers located across the U.S. and Canada. It also happens to have $1.8 billion of debt. The company is equally owned by private equity firms Ares Management LP and TPG Capital.
The debt — coupled with the loss of a major customer — is a big concern. More from Crain’s,
But ATD's capital structure is stretched tight, said Lawrence Orlowski, a director in corporate ratings at S&P. While the company has access to $465.4 million in asset-based lending facilities and $22.7 million in cash as of the end of 2017, even that liquidity may not be enough to stay solvent if ATD permanently loses Goodyear's business or if any other major tire makers pressure the company for concessions, according to Orlowski.
Something tells us (restructuring) advisors may be circling around trying to determine whether it can get together a group of the company’s term lenders.
*****
Second, Tweddle Group Inc., a The Gores Group-owned manufacturer of automotive owners’ manuals (that nobody ever reads) likewise suffered a disastrous blow when Fiat Chrysler Automobiles N.V. announced back in April that it was no longer using Tweddle’s services. Fiat reportedly accounted for 40% of Tweddle’s 2017 revenue and will be hard to replace. Consequently, Moody’s issued downgrades noting,
“The downgrades reflect a credit profile that is expected to be significantly weakened following Tweddle's loss of certain work from a key customer, and the resultant mismatch between the company's earnings and cash flow prospects and its now much more levered balance sheet.”
This reportedly put pressure on the company’s $225mm ‘22 first lien term loan and now the company reportedly has hired Weil Gotshal & Manges LLP for assistance. While it will likely take some time for the loss or revenue to trip any leverage ratios in the company’s credit agreement, this is a name to watch.
*****
Finally, Bloomberg New Energy Finance recently released its “Electric Vehicle Outlook 2018” report. Therein in noted that there are a variety of factors driving EV sales forward:
Lithium-ion battery prices have tumbled, dropping 79% in seven years. Meanwhile, the batteries’ energy density has improved roughly 5-7% per year.
Chinese and European policies are pushing fleet electrification.
Automakers are aggressively pushing the electrification of their fleets. Choice bit: “The number of EV models available is set to jump from 155 at the end of 2017 to 289 by 2022.”
Bloomberg notes:
Our latest forecast shows sales of electric vehicles (EVs) increasing from a record 1.1 million worldwide in 2017, to 11 million in 2025 and then surging to 30 million in 2030 as they become cheaper to make than internal combustion engine (ICE) cars.
Marinate on that for a second. That is a massive 10x increase in the next 7 years followed by an additional 3x increase in the following 5 years.
Bloomberg continues,
By 2040, 55% of all new car sales and 33% of the global fleet will be electric.
But what about President Trump (#MAGA!) and efforts to limit future alternatives subsidies?
The upfront cost of EVs will become competitive on an unsubsidized basis starting in 2024. By 2029, most segments reach parity as battery prices continue to fall.
So, sure. Distressed activity thus far in 2018 has been light in the automotive space. But dark clouds are forming. Act accordingly.
Fast casual is supposed to be a bright spot for restaurants. But as the segment has grown in recent years, there are bound to be winners and losers. Zoe’s Kitchen Inc., a fast casual Mediterranean food chain with 250 locations in 20 states ($ZOES), is increasingly looking like the latter.
Last week the company reported sh*tty earnings. Comp restaurant sales declined by 2.3% despite rising prices pushed on to the consumer. The decline is attributable to the usual array of externalities (e.g., weather) but also location cannibalization. Apparently, the company’s growth strategy is pulling consumers from previously established locations. Moreover, the company noted “inflationary pressures in produce and freight costs, that are expected to impact cost of goods sold for the balance of the year.” Wages also increased 3.3%, an acceleration from the 2.9% realized in Q4 ‘17. Accordingly, adjusted EBITDA decreased 30.9%. The net loss for the quarter was $3.6mm or -$0.19/share. The company lowered guidance. The stock tumbled.

Before you get too excited, note that this is a debt-light company: it currently has a ‘22 $50mm revolving credit facility with JPMorganChase Bank NA, of which $16.5mm is outstanding (with $3.7mm of cash on hand, net debt is only $12.8mm). It also, believe it or not, has covenants — leverage and interest coverage, among others — and the company is in compliance as of April 16, 2018. It also plans to continue its expansion: in the sixteen weeks ended 4/16/18, the company opened 11 company-owned restaurants with a plan to open approximately 25 (inclusive) over the course of fiscal year ‘18. That said, it does intend to rationalize existing locations (and expects some impairment charges as a result), cut G&A and take other operational performance improvement measures to combat its negative trends. There’s a potential opportunity here for low-to-middle-market FAs and real estate advisors.
For our part, we found this bit intriguing (unedited):
We are definitely seen more competitive intrusion, more square footage growth in some of those smaller kind of mid to kind of large markets where we've been there for some time now that's a little bit of what we're seeing in those markets.
We've also seen more competitive catering competition as every ones ramped up catering. And also the value and discounting as we spoke to in the call, in the prepared remarks we've seen that $10 check with that single user kind of moving around and we think that's so from the new competition square footage growth, the value and discounting and then the delivery interruption, we've seen or felt that in many of our markets.
There’s a lot to unpack there. Clearly competition, as we noted upfront, is increasing in the $10-check size cohort of fast casual. Catering is always a competitive business for restaurants like this too. But, the point that really got out attention was that about delivery. The company says pointedly, “We also believe that disruption from delivery and discounting has created headwinds.” The company further states,
Digital comps were 26% positive in Q1 as we leverage improvements from last year's investments in web and mobile platforms to build greater convenience for our guests. Early in Q2, we relaunched and upgraded our loyalty program, which is expected to help drive traffic by making it easier and clearer for our guest to earn and redeem rewards. Delivery sales grew in both our non-catering and catering businesses by 155%. And we have a clear plan to build out the channel for more profitable growth in 2018.
The impact of mobile food ordering and the need for delivery cannot be overstated. Companies need to act fast to activate delivery capabilities that makes sense to a mobile consumer who, more and more, goes to Postmates, Caviar, UberEats and other food delivery services for discovery. This is precisely why Shake Shack ($SHAK) is now on Postmates and Chipotle Mexican Grill Inc. ($CMG) is now available on Doordash. Others, like privately-owned Panera Bread are taking a step farther by building out its own delivery infrastructure in an attempt to own all its data and deliver without owing a cut to a middleman. Query whether this is far too much dependence on the likelihood of people to go directly to Panera’s app when they’re hungry…?
It sounds like the Zoe folks are increasing their focus on delivery. The question is whether they can execute fast enough to offset in-store dining declines. And whether they can do it on their own.
Subscription-based razors? Check. Subscription-based contact lenses? Check. Now the direct-to-consumer digitally-native-vertical-brand world is coming for your teeth. Direct to consumer teeth alignment? Check. Subscription-based dental floss? Check. Subscription-based bluetooth compatible toothbrushes. Check. No. This is not a joke.
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.

Do y’all remember the segway? It was supposed to revolutionize transportation but it never took off as anything more than the butt of a joke. Why? Look at the above photo. Homeboy can pump as many curls as he needs to but all the bulging biceps in the world won’t make him look bada$$ riding one of those things. Plus, watch the eye level broheim.
Anyway, there is a new mode of transportation that is all the rage. Introducing the dockless electric scooter…

To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
Ok. Soooooo…this won’t shock anyone who has been paying attention. Apparently Moviepass — the company that lets subscribers see one movie a day for only $9.99 a month — is burning cash like nobody’s business. S.H.O.C.K.E.R. A first grade student can do THAT math.
Moviepass’ parent company Helios and Matheson Analytics Inc. ($HMNY) reported in an 8K filed this week that it burned $21.7 million per month from September 2017 through April 2018. The company now has $15.5 million in available cash with another $27.9 million in accounts receivable. Hang on: 15.5 + 27.9 (carry the four) = 43.4. Minus 21.7 and another 21.7 and….💥🔥💥🔥. Which prompted CNN to ask, “is the end near?” Here’s a choice quote...
To continue reading, you must be a PETITION Member. Become one here.
On Mary 15, 2017 - nearly exactly a year ago — rue21 Inc. became the latest in what was a string of specialty fashion retailers to file for bankruptcy; it sought to pursue both an operational and a financial restructuring. The company had 1179 brick-and-mortar locations in various strip centers, regional malls and outlet centers. It also had a capital structure that looked like this:

Much of the leverage emanated out of an Apax Partners LLP-sponsored take-private transaction in 2013. We recently discussed Apax Partners in the context of FullBeauty here, in our recent Members’-only briefing.
Without any real contest, it was clear that the term loan holders constituted the “fulcrum” security and would end up swapping said loans for equity in the reorganized company. And that is precisely what happened. The ABL was covered, the term lenders funded a roll-up DIP credit facility along with new money to finance the pendency of the cases and then converted that DIP into an exit facility. The post-emergence capital structure consists of:
$125 million ABL; and
$50 million term loan (plus accrued interest on the DIP term loan as of the effective date).
General unsecured claimants were provided an equity “kiss” on the petition date and then, after the Official Committee of Unsecured Creditors’ (“UCC”) formed, it extricated additional value in the form of, among other things, (i) a put option to sell its post-reorg equity to one of the reorganized debtors, and (ii) a waiver by the prepetition term lenders of their $200 million deficiency claim. While the UCC did try and go after third-party releases for Apax, Apax ultimately succeeded in obtaining the release pursuant to the bankruptcy court’s September 9 confirmation order on the basis that it…
“…agreed to (i) support the Plan, including by promptly facilitating and participating in prepetition Plan discussions that culminated in the Restructuring Support Agreement and the Plan, notwithstanding that their equity position would likely be eliminated thereunder; and (ii) participate in the financing of the DIP Term Loan Credit Facility.”
In other words, Apax bought its release for $2 million in DIP allocation.
All told, this was a solid deleveraging of roughly $700 million. Moreover, the company closed roughly 400 stores. The company was seemingly well-positioned to effectuate the rest of its proposed restructuring, including (i) revamping its e-commerce strategy, (ii) improving the in-store experience, and (iii) pursuing a long-term business plan under relatively new management in a highly competitive retail atmosphere.
“Seemingly” being the operative word. In January, The Wall Street Journal reported (paywall) that the retailer experienced lackluster sales and tightening trade terms. Then, in February, Reuters reported that the company “is seeking financing after lackluster holiday sales failed to generate the cash it had hoped for….” It noted, further, that the company had engaged Piper Jaffray Companies ($PJC) to raise the funds. Notably, there has been nothing new on this front since. No news is probably not good news when it comes to this situation. Start the sewing machines: a Scarlet 22 tag may be in order and a liquidation on the horizon.
In the meantime, if the company is looking for ways to preserve liquidity, it might want to consider a far less generous return policy:

With clothes like this and a customer like that, what could go wrong?
Back in “WeWork Invents a New Valuation Methodology,” we snarked about how WeWork pioneered an entirely new valuation technique. We noted,
"Indeed, to assess WeWork by conventional metrics is to miss the point, according to Mr. Neumann. WeWork isn’t really a real estate company. It’s a state of consciousness, he argues, a generation of interconnected emotionally intelligent entrepreneurs. And Mr. Neumann, with his combination of inspiration of chutzpah, wants to transform not just the way we work and live, but the very world we live in.”
A state of consciousness. A state of effing consciousness. Being a biglaw associate is also a state of consciousness but that doesn’t necessarily mind-port you to partner after 8 years, let alone 12.
We continued,
"Even Adam Neumann, a co-founder of WeWork and its CEO, admits that his company is overvalued, if you’re looking merely at desks leased or rents collected. ‘No one is investing in a co-working company worth $20 billion. That doesn’t exist.’ he told Forbes in 2017. ‘Our valuation and size today are much more based on our energy and spirituality than it is on a multiple of revenue.'“
We’re sure bankers all across the world will be happy to add “energy and spirituality analysis” to the lineup of valuation methodologies like precedent transaction, comparable company and discounted cash flow analyses. What the bloody hell.
Then last Wednesday, in 💵WeWork Taps Cap Markets; People Lose Minds 💵, we briefly covered the proposed WeWork’s proposed $500 million high yield bond issuance. People went nuts because the offering memorandum finally shed some more light on the business. And it was a feeding frenzy. Little did we know, that was only Part II of this (unintentional) comedy.
Introducing “Community-adjusted EBITDA.” Per Barron’s:
As The Wall Street Journal reported, while revenue doubled last year, to $866 million, WeWork’s losses also doubled, to $933 million. But WeWork “earned $233 million, based on a metric the company dubbed “community adjusted Ebitda.” That consists of earnings before interest, taxes, depreciation, and amortization — a widely used measure of operating cash flow — but also excludes basic operating expenses, such as marketing, general and administrative, development, and design costs. That’s not in any accounting textbooks I’m aware of.
“I’ve never seen the phrase ‘community adjusted Ebitda’ in my life,” said Adam Cohen, founder of Covenant Review, a bond research company.
There’s a first time for everything, homie. Or as Bloomberg’s Matt Levine put it,
Well, sure, Mr. Covenant Review, but I bet you’ve never reviewed the covenants of a state of consciousness either.
Some more choice commentary:
Indeed, Moody’s was mildly schizophrenic (registration required) in its evaluation of the company’s new notes; it didn’t deign to even discuss WeWork’s accounting gymnastics as it assigned a B3 Corporate Family rating and a Caa1 rating to the notes.
Dealbreaker’s Thornton McEnery was far less measured. In lofty prose worthy of a Pulitzer, he led his piece entitled “WeWork’s First-Ever Bond Offering Is A Master Class in Financial Masturbation” with “[n]o company has its head farther up its own ass than WeWork.” We literally laughed out loud at that. But wait. There’s more,
That said, making up your own holistic, artisan, New Age Brooklyn accounting principle just to pretend that you’re hemorrhaging less money than you really are? Well, that’s actually super-ballsy and we’d almost respect it if WeWork wasn’t trying to write down Kombucha on tap and losses associated with ping pong ball replacements. It’s the height of Millennial hipster exceptionalism and it would truly make our skin crawl if, again, we didn’t respect the balls-out ego involved here.
Can you even say “balls-out” anymore? We thought #MeToo killed that. And ping pong? C’mon. That’s so 2014. It’s esporting Fortnite matches that are all the rage now, broheim. Anyways…
Then Bloomberg’s Matt Levine and Axios’ Dan Primack crashed the party by issuing a bit of defense. Levine’s is here — noting that the calculus is a bit different for bond investors. Primack spoiled some of the fun by clarifying what the new-fangled metric represents:
The metric includes all tenant fees, rent expense, staffing expense, facilities management expense, etc. for active WeWork buildings.
The exclusions are company-wide expenditures, which do not get pro rated. Much of that relates to growth efforts, although not all of it (executive salaries, for example).
One comp, and its not perfect, could be how Shake Shack reports "shack-level operating profit margins."
Bottom line: It's still kind of silly, but less silly than it at first appears. And obviously the ratings agencies and bond markets didn't seem put off.
Silly? Less silly? Whatevs.
Either way, the Twitterati largely neglected to take into account today’s dominant theme-among-themes: yield, baby, yield. Or said another way — per The Financial Times,
WeWork does have substantial backing, blue-chip customers and a good plan to increase profit-sharing leases. A high yield in its first bond, adding 150 basis points or so to the index average yield, would help, too. That could swell the offer above $500m. Even sober bond investors may not prove immune to the appeal of succulents and exposed brick.
Prescient. And bond investors did not prove immune. Nor sober.
Welcome to Part III. This is the part in the story where the record scratches, the jukebox stops, and everyone has an utterly perplexed look on their faces. Like, wait. WHAT? That’s right. Demand for this paper was so high, that it upsized from $500 million to $702 million. And just like that, poof! Adam Neumann looks into the camera, smirks, and then walks down the street like Kaiser-m*therf*ckin-Soze. He can tap the venture capital markets — stateside and abroad (in the case of Softbank) — and the debt market.
The Real Deal somewhat inexplicably stated,
WeWork sold $700 million in bonds Wednesday to investors wary of another startup with unstable cash flow entering the debt market.
Wary? How do you explain the upsized offering then? The only thing people should be wary of are other people who are shocked to see this happening. Again: YIELD. BABY. YIELD. And, to be clear, it was actually $702 million (at 7.785%). The notes are guaranteed by US subsidiaries that hold approximately 60% of the company’s assets at year end; “adjusted ebitda” was also used as the base for leverage requirements under the notes’ covenants. There’s hair all over this thing. The Financial Times took a deeper dive into lender protections as it…
wanted to get a general idea of the rights its bondholders might have if the bonds were sold under the terms laid out in the preliminary prospectus and then Millennials everywhere suddenly decided they would prefer to work from home.
Right, exactly. Or in a cafe where you can sit for hours for $3/day. Anyway, you can read that FT analysis here. Moreover, BloombergGadfly cautions about the rent duration mismatch here — a subject of particular note for restructuring professionals well-versed in section 365 of the bankruptcy code. Bloomberg notes,
WeWork acknowledges that its expenditures "will make it difficult for us to achieve profitability, and we cannot predict whether we will achieve profitability in the near term or at all." Risk is all part of the game for junk investors, and this one looks like it will be priced to go with a fat yield. But the more prudent will take that caveat seriously.
Investors must’ve REALLY wanted in on the action. Many didn’t take that caveat seriously. Something tells us Burton Malkiel will be adding an addendum to his “Greater Fool Theory” coverage in “A Random Walk Down Wall Street” and this will be the case study.
What explains the enthusiasm? As The Wall Street Journal notes, this isn’t a $20 billion decacorn-x2 for nothing:
The numbers offer some positive signs for WeWork. Its net construction costs per desk fell 22% in 2017 to $5,631. And its corporate business—as opposed to revenue from freelance and small companies—appears to be growing well, as rating agency Standard & Poor’s said in its analysis. The agency said it expects large corporations will occupy 50% of WeWork’s desks within two years, up from 25% today.
But then they flip right around and note,
There also are concerns for investors in WeWork’s growth trajectory. Its revenue per user fell 6.2% to $6,928 in 2017, while sales-and-marketing costs more than tripled to $139 million, representing 16% of revenue, up from 9.9% in 2016.
Taking on debt adds risk to a company whose business model hasn’t been tested in a downturn. Given that its members typically sign monthly or annual leases, a drop in demand during a recession would mean the rents it charges tenants would fall, while the payments it owes to landlords would stay constant.
Nevertheless, the market spoke. It gobbled up those bonds.
But then, in Part IV, the market spoke again, mere days later. As Bloomberg noted,
WeWork Cos.’s bonds extended their losses on Tuesday, as investors who were at first enthused to get a piece of the action have since been cashing in their chips.
The $702 million of speculative-grade bonds, which sold last week at par, fell for the fourth straight day on Tuesday to 95.75 cents on the dollar, according to Trace bond-price data. That’s a sharp contrast to the outsized orders the company saw when it marketed its debt in primary markets last week.
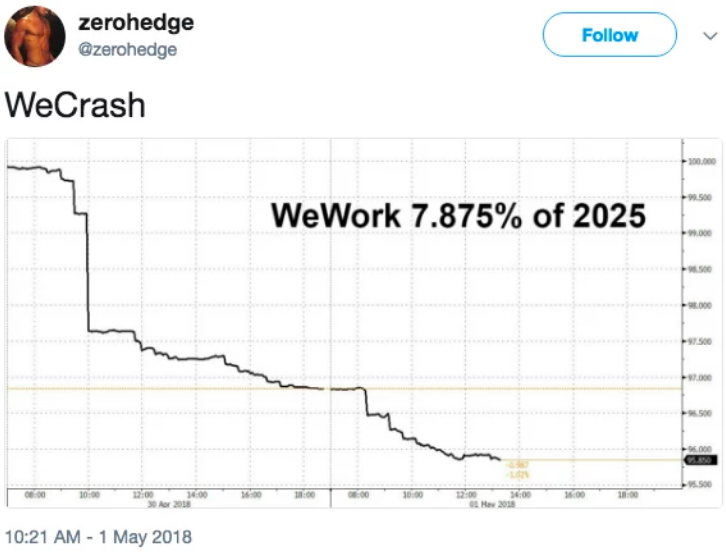
And then they kept falling.

Source: Bloomberg
Per Trace, the bonds last printed on Friday, May 4 at 94.9 — a pretty impressive decline on the week (h/t @donutshorts).
This sequence of events likely has bondholders screaming, “Yield, baby. YIELD!!!”
-----
PETITION is twice-weekly newsletter covering disruption from the vantage point of the disrupted. We meander sometimes to other areas. This piece was in today's Members'-only newsletter. You can check us out here and follow us on Twitter here.
In “Credit Default Swaps (Long Yield, Baby, Yield),” we discussed credit default swaps and the ongoing battle between hedge funds in the Hovnanian matter.* The Commodity Futures Trading Commission has finally weighed in. There were no minced words:
"The CDS market functions based on the premise that firms referenced in CDS contracts seek to avoid defaults, and as a result, the instruments are priced based on the financial health of the reference entity. However, recent arrangements appear to involve intentional, or ‘manufactured,’ credit events that could call that premise into question. In a public statement dated April 11, 2018, the International Swaps and Derivatives Association’s (ISDA) board of directors criticized manufactured credit events, writing that they ‘could negatively impact the efficiency, reliability, and fairness of the overall CDS market,’ and ISDA’s board indicated that it advised its staff ‘to consult with market participants and advise the Board on whether...amendments to the ISDA Credit Derivatives Definitions should be considered’ to address manufactured credit events.
"Manufactured credit events may constitute market manipulation and may severely damage the integrity of the CDS markets, including markets for CDS index products, and the financial industry’s use of CDS valuations to assess the health of CDS reference entities. This would affect entities that the CFTC is responsible for overseeing, including dealers, traders, trading platforms, clearing houses, and market participants who rely on CDS to hedge risk. Market participants and their advisors are advised that in instances of manufactured credit events, the Divisions will carefully consider all available actions to help ensure market integrity and combat manipulation or fraud involving CDS, in coordination with our regulatory counterparts, when appropriate.”
Better late than never we guess. You’d think they would have awakened to these issues after Codere, Radio Shack, and others. But, hey. Regulators. Enough said.
*****
Enough said, indeed. Query whether the The Commodity Futures Trading Commission will have more to say given the aforementioned “cherry on top” in the McClatchy transaction.
What is the cherry? Well this — per Bloomberg:
It seemed like a sure-fire bet: short the debt of a highly leveraged newspaper company that’s losing money. And for a while, it worked as investors piled up almost $500 million of wagers by buying credit-default swaps on the publisher, McClatchy Co.
That is until hedge fund Chatham Asset Management stacked the deck with a deal that’s threatening to make those swaps all but worthless.
The McClatchy situation is the latest trade that’s drawing jeers from critics who say the $11 trillion CDS market has devolved into a haven for manipulation.
Whoops.
At issue is the “newly established LLC” bit we noted above. As Bloomberg further explains,
Because the new debt would be shifted away from the parent and into the new unit, it’s fueling speculation that the Chatham deal will create what’s commonly known in the CDS world as an orphaned contract. In other words, anyone who bought insurance on a McClatchy default would effectively be paying insurance on an entity with no significant debt.
Which, naturally, begs the question: who is on the other side of the contract? Well, Chatham, of course. Because CDS! There’s no measure of how America has become great again like one fund ripping off other funds. Take a look at this chart:

More from Bloomberg,
Leading up to the deal, Chatham had been selling swaps insuring against a default by McClatchy. So if the transaction were to be completed, it would be getting paid CDS premiums to guarantee against a default that could never technically happen.
“The whole market is losing credibility when you have events like this where you try to trigger the CDS or create orphaning situations,” XAIA’s Felsenheimer said.
Joshua Friedman from Canyon Partners appears to agree that these trades “go beyond the bounds” (video). And, so, people are losing their minds (query whether these same people led to the upsized WeWork debt financing). As always, Matt Levine puts this whole event in perspective,
The thing is, if you bet against McClatchy’s credit by buying CDS on it, you were betting not only that it would have problems with cash flow or whatever, but also that no white knight would come along to keep it afloat until after your CDS expired. A realistic credit analysis asks not only about the company’s own paying capacity but also about its external sources of financing. If you buy five-year CDS on a company, you are betting that it will default on its debt within five years. If the next day a deep-pocketed shareholder (Chatham owns 19.8 percent of McClatchy) refinances all of the company’s debt into a seven-year zero-coupon bond—or a seven-year PIK-toggle bond, or whatever, some form of debt that it cannot default on during the life of the CDS—then you have lost your bet. But you weren’t cheated out of your bet or anything. You just bet that the credit would implode, and then it didn’t.
He’s right. And in the absence of regulators paying more attention to CDS work-arounds, this will be just one more needle in a stack of perceived-manipulated-needles.
*Yesterday, Hovnanian upheld its end of the bargain with GSO by skipping its interest payment.
The McClatchy Company ($MNI) may not be well known to you on its face but if you’ve ever read the Miami Herald, The Kansas City Star, The Sacramento Bee, The Charlotte Observer, The (Raleigh) News and Observer, The (Fort-Worth) Star-Telegram, The (Durham NC) Herald-Sun or one of 24 other media companies, you’ve read one of its properties. It is a provider of digital and print news and advertising services. And it reported Q1 earnings last week.
The earnings — as you might imagine for a company with a large print-media division — were far from gangbusters and are highly cyclical in nature. Take a look at this chart:

The company missed estimates on both EPS and revenue. Total revenues were down 10.1% YOY. Total advertising revenues were down 16.7% YOY. Direct marketing advertising revenues declined 21.9% YOY. On the flip side, the company experienced growth in its digital initiatives, including increases in digital-only subscribers and average total unique visitors to online properties. The company also partnered with Subscribe with Google to push further improvements in the digital business. But, all in, this is a company that it is facing a massive wave of disruption coming at it from all angles.
First, its capital structure. The company’s leverage ratio stands at 4.42x as of the end of Q1 on the basis of its existing cap stack. Currently, it has about $30 million of outstanding letters of credit issued against its $65 million revolving credit facility (Bank of America). As of 12/31/17, the company had $344.6 million of 9% ‘22 senior secured first lien notes outstanding on top of (a) as of 4/27/18, $82.1 million of 7.15% ‘27 debentures and (b) $274 million of 6.875% ‘29 indentures.
But, not for long. Enter Chatham Asset Management. The fund — which may or may not be fresh off of a shiny new $1b private equity vehicle for debt-related investments — is taking out a large chunk of the capital structure. The company filed an 8k on April 26th, indicating that there is a term sheet pursuant to which a newly established LLC will issue $250 million of 7.372 % ‘30 Tranche A Term Loan paper and $168.5 million 6.875% ‘31 of Tranche B Term Loan paper, the proceeds of which will be used to take out the long-dated debentures (except $8.3 million) and a portion of the senior secured notes. The structure isn’t yet determined but the interest expense is expected to increase incrementally. There is a makewhole as well, as you might expect, and we’re guessing it will have some fairly iron clad verbiage. In other words, this reeks of loan-to-own — with a cherry on top (see #2 below). Perhaps Chatham will eventually roll up the properties with American Media Inc., parent to The National Enquirer, which Chatham owns 80% of and, per The Wall Street Journal, appears to be having issues of its own.
Some notable bits in the company’s earnings call:
A. Tariffs. Tariffs on newsprint may have an effect on traditional print media companies. Note the following comments:
One more word on the print newspaper world. We are often asked on these calls about the impact of newsprint prices on our operating model. As the print side of our business has declined so has our operating sensitivity to fluctuations in newsprint supply and pricing, now less than 4% of our operating expense, down from 20% at the peak of print newspaper revenues more than a decade ago.
Nonetheless, policies such as the newsprint tariffs announced by the administration earlier this year are unhelpful we believe, both to free market and to public policy. We oppose them and we have made our position clear to the administration. We say this as an equity owner of one of the few remaining U.S. domestic newsprint producers. So one might assume we would be on the other side of this issue, but we are not. Public policy that makes these input prices more costly at a time of great stress in this industry harms our local communities and is against the public interest.
Interesting. The company is guiding towards higher print costs, including increases in pricing coming from Canadian mills. #MAGA!!
B. Cost Controls. This company has all of the makings of a company in triage. Operating expenses were down 8.4%. The company outsourced printing operations. It entered into a sale leaseback transaction, pursuant to which $13 million of proceeds is being offered to the company’s senior secured noteholders in a tender offer at par. It sold off some intellectual property (CareerBuilder LLC). All of this is meant to buy the company time to effectuate its digital transformation.
C. Ad Spend. This should come as a surprise to nobody that follows the world of restructuring but the trickle-down effect of battered grocery and retail is notable here. This is the company’s statement about the higher-than-expected ad spend decline:
I mean retail results were disappointing. Obviously, that’s something that we’ve been seeing for some time now. Total retail revenues finished a bit better actually in Q1 and Q4, but that was driven entirely by digital growth. Revenue from preprints delivered with the newspaper actually got worse. And as Elaine said, our direct marketing circulars delivered to non-subscribers also softened. So our retail customers are facing some tough citing and it continues to have an impact on our print products. And some of those advertisers obviously in direct marketing are the same as the ones that are in the print newspaper, and their troubles affect both.
In retail print revenue, our largest declines were coming from the food and drug department store category, and we’ve seen that strand for a while. Preprints took a steeper decline in Q1. And then we’ve seen in previous quarters down about 38% over last year. Again though due to continued losses from the major department stores like Macy's, Sears, Stein Mart, Penne and stores no longer in business that were rolling over from last year like hhgregg and Toys "R" Us, or at least going in bankruptcy, Toys "R" Us is still struggling.
And so in preprints or about 12% of total advertising revenues, so when that gets hit that’s of percentage, it takes the whole category down. So mostly I think a story on the retail side, Avi, and continuing pressure on the print part of that business.
The company continued,
We sometimes talk about the importance of our role in local communities and with our neighbors, and these are the places we live where our employees are residents all across the country. The impact on local retail across the country has been, as you know, very widespread. This is an earnings call about a news and information company. So it’s the wrong place to talk about those underlying trends. But I would say we’re super aware of them. We obviously bare the impact from an advertising perspective, which also having a big impact on our communities. And that’s something that we’re extremely aware of as in many cases the leading local news and information company in those communities.
We appreciated the reminder. Jokes abound about the #retailapocalypse. For many local communities, the far-reaching effects of such are no laughing matter.
In “The Latest and Greatest on Guitar Center,” we cast some shade on the guitar retailer’s amend-and-extend transaction. We wrote,
On Monday, Guitar Center — with the help of bankers UBS and Houlihan Lokey and the consent of Ares — launched an exchange offer and consent solicitation related to its unsecured notes. The offer is to swap the existing $325 million 9.625% notes for $325 million of 5% cash/8% PIK notes due 2022 (along with with some warrants). Per the company’s press release, $299 million worth of holders have already agreed (92% of the issuance). This swap would save the company $13,812,500 a year in interest expense AND have the effect of pushing out the maturity for three years. Gotta love the capital markets these days.
In tandem, the company is proposing to offer $635 million of new 9.5% senior secured notes due 2021. The use of proceeds of these new notes would be to redeem the $615 million 6.5% senior secured notes due 2019. With this piece of the transaction, the company will be taking on an additional $20.35 million of annual interest expense.
Finally, the company will also refinance the $375 million ABL, extending the maturity out by 5 years.
So, if you made it this far, here’s the upshot: if these transactions are successful, the company will have availed itself of a few years to turn itself around by pushing out its debt maturities. But, it will have eliminated ZERO INTEREST EXPENSE in the aggregate. Said another way: this is a band-aid, not a solution.
All of which means that the company needs to hope and pray some rock God hits the scene and reinvigorates the market for guitars in the next two years. We’ll take the under.
As it turns out, the company ultimately downsized the amount of 5% cash/8% PIK notes due 2022 from $325 million to $318 million which will, naturally, have the affect of...to read this rest of this a$$-kicking commentary, you must be a Member...

On Wednesday, we concluded the “DO. NOT. MESS. WITH. DAISY. CHAPTER 2 (Short Pet Retailers 2.0) 🔫🔫” about Petsmart Inc., with the following statement:
“With 1600 stores, the company isn’t light with its footprint and same store sales and pricing power are on the decline. Still, the company’s liquidity profile remains relatively intact and its services businesses apparently still drive foot traffic. Which is not to say that the situation doesn’t continue to bear watching — particularly if Chewy.com’s customer-acquisition-costs continue to skyrocket, overall brick-and-mortar trends continue to move downward, and the likes of Target ($T), Walmart ($WMT) and Amazon ($AMZN) continue to siphon off market share. A failure to stem the decline could add more stress to the situation.”
Well, guess what: industry trends are continuing to decline. Last week Petco Holdings announced dogsh*t earnings (oh man, we’ve been waiting all week for that…SO GOOD) and, suffice it to say, its (and Petsmart’s) bonds made fresh lows on the news.
To read this rest of this a$$-kicking commentary, you must be a Member...

On this day exactly one year ago, Recode first reported that Petsmart acquired Chewy.com for $3.35 billion — the “largest e-commerce acquisition ever.” Venture capitalists — and the founders — of course, rejoiced. This was an a$$-kicking exit — particularly for a company that, at the time, was only six years old. The reported amount of venture funding topped out at $451 million, a massive sum, but sufficiently low enough for the VCs to make a substantial return. Recode wrote,
“The deal is a huge one by any standard — bigger than Walmart’s $3.3 billion deal for Jet.com last year — and especially for a retail company like PetSmart, which was itself valued at only $8.7 billion when private equity investors took it over in 2015.
But Chewy.com has been one of the fastest-growing e-commerce sites on the planet, registering nearly $900 million in revenue last year, in what was only its fifth year in operation. The company had been a potential IPO candidate for this year or next, but was taken out by its brick-and-mortar competitor before that. It was not profitable last year.”
Recode continued,
“The deal seems like the type of bet-the-company acquisition by a traditional retailer that commerce-focused venture capitalists have been betting on for some time. While Walmart’s acquisition of Jet.com was a huge deal by e-commerce standards, it represented just a fraction of Walmart’s market value.”
Toss of the dice notwithstanding, most talking heads seemed to think that the acquisition made “strategic sense.” Nevertheless, Recode’s sentiment was more prescient than they likely suspected — mostly due to the havoc it has wreaked to Petsmart’s cap stack.
The company financed the purchase with a two-part debt offering of (a) $1.35 billion of ‘25 8.875% senior secured notes and (b) $650 million of ‘25 5.875% unsecured notes. Rounding out the capital structure is a $750 million ABL, a $4.3 billion cov-lite first-lien term loan and $1.9 billion cov-lite ‘23 senior unsecured notes. Let us help you out here: 1+2+3+4 = $8.2 billion in debt. The equity sponsors, BC Partners, GIC, Longview Asset Management, Caisse de dépôt et placement du Québec and StepStone Group, helped by writing a $1.35 billion new equity check. So, what did all of this financing lead to?
One year later, CEO Michael Massey is gone and hasn’t been replaced. More recently, Ryan Cohen, the CEO and co-founder of Chewy.com has departed. Blue Buffalo Pet Products Inc., which reportedly accounted for 11-12% of PetSmart’s sales, opted to supply its food products to mass-market retailers like Target ($T) and Kroger ($KR). The notes backing the Chewy.com deal are trading (and have basically, since issuance, traded) at distressed levels. Petsmart’s EBITDA showed a 34% YOY decline in Q3. And, worse even (for investors anyway), the bondholders are increasingly concerned about asset stripping to the benefit of the company’s private equity sponsors. S&P Global Ratings downgraded the company in December. It stated,
“The downgrade reflects our view that the capital structure is unsustainable at current levels of EBITDA, although we do not see a default scenario over the next year given liquidity and cash generation. Such underperformance came from the company's rapid e-commerce growth that generated higher losses, and unanticipated negative same-store sales at its physical stores. As Chewy aggressively expands its customer base, we believe operating losses will widen because the company has not yet garnered the size and scale to offset the unprofitable business volume from new customers.”
Financial performance and ratios were a big consideration: margin is compressed, in turn negatively affecting the company’s interest coverage ratio and leverage ratio (approximately 8.5x).
Moody’s Investor Service also issued a downgrade in January. It wrote,
“We still believe the acquisition of Chewy has the potential of being transformative for PetSmart as it will exponentially increase its online penetration which was previously very modest. However, as Chewy continues to grow its topline aggressively and incur increasing customer acquisition costs we expect its operating losses to increase. More importantly, the increasingly competitive business environment particularly from e-commerce and mass retailers has led to increased promotional activity which has negatively impacted PetSmart's top line and margins. We expect this trend to continue in 2018.”
Bloomberg adds,
“Buying Chewy.com was supposed to be a coup for PetSmart Inc. For debt investors who funded the deal, it’s been more like a dog.”
See what they did there?
With 1600 stores, the company isn’t light with its footprint and same store sales and pricing power are on the decline. Still, the company’s liquidity profile remains relatively intact and its services businesses apparently still drive foot traffic. Which is not to say that the situation doesn’t continue to bear watching — particularly if Chewy.com’s customer-acquisition-costs continue to skyrocket, overall brick-and-mortar trends continue to move downward, and the likes of Target ($T), Walmart ($WMT) and Amazon ($AMZN) continue to siphon off market share. A failure to stem the decline could add more stress to the situation.
*****
💥We’ll discuss Petco Holdings in “DO. NOT. MESS. WITH. DAISY. CHAPTER 3 of 3 (Short Pet Retailers 2.0) 🔫🔫🔫” in our Members’-only briefing on Sunday.💥

We have covered a lot of ground since our inception and, for the most part, the path has been trodden with depressing stories of disruption and destruction. The root causes of that run the gamut - from (i) Amazon ($AMZN) and other new-age retail possibilities (e.g., resale and DTC DNVBs) to (ii) busted PE deals to (iii) fraud and mismanagement. Through it all, nothing has really gotten us too fired up — not the hypocrisy surrounding Bank of America’s ($BAC) loan to Remington Outdoor or the hubris around Toys R Us. But, once you start effing with our dogs’ diets, that’s when we have to start getting all-John-Wick up in this mofo.
Enter PFS Holding Corp., otherwise known as Phillips Pet Food & Supplies (“PFS”). PFS is a distributor of pet foods, grooming products and other useless over-priced pet gear. It is private equity-owned (sponsor: Thomas H. Lee Partners) and has $450+ million of LBO-vintage debt spread out across a recently-refinanced $90 million revolving credit facility (pushed to 2024 from January 2019), a cov-lite ‘21 $280 million term loan, and a cov-lite ‘22 $110 million second lien term loan.
The company recently got some breathing room with a freshly refi’d revolver but still has some issues. While quarterly sales increased in Q4 from $293 million to $327 million, gross margins were down — a reflection of price compression. EBITDA was roughly $62 million on a consolidated adjusted basis clocking the company in at right around a 7.4x leverage ratio. The ‘21 and ‘22 term loans both trade at distressed levels, reflecting the market’s view of the company’s ability to pay the loan in full at maturity. Upon information and belief, the new revolver includes a 90-day springing maturity which means that the company is effed if it is unable to refi out the term loan prior to its maturity (which, admittedly, seems lightyears away from now).
All in, S&P Global Ratings appears to think that the Force is weak with this one; it issued a corporate downgrade and a term loan downgrade of the company on April 10, 2018. Why? Well, S&P doesn’t pull any punches:
“The downgrade reflects our view that, absent significantly favorable changes in the company’s circumstances, the company will seek a debt restructuring in the next six to 12 months, particularly given very low trading levels on its second-lien debt, between 30 and 40 cents on the dollar. It also reflects our view that cash flow will not be sufficient to support debt service and maintain sufficient cash interest coverage, resulting in an unsustainable capital structure. We forecast adjusted leverage in the mid-teens. PFS recently lost a substantial portion of business with one of its largest customers, which we believe represented over half of the company’s EBITDA. Management implemented several cost savings initiatives last year, but we do not believe savings achieved will be sufficient to offset this dramatic profit loss. Further, we expect the company will continue to be pressured by a secular decline in the independent pet retail market, which we view as PFS’ core customer base. Independent pet shops continue to lose market share to e-commerce and national pet retailers, as consumer adoption of e-commerce for pet products purchases grows.”
There’s a lot there. But, first, who writes these dry-as-all-hell reports? If any of you has a connection at S&P, consider putting us in touch. We could really spice these reports up.
Here’s our take:
“The downgrade reflects the fact that this business is turning into garbage. The company was hyper-correlated to one buyer, is over-levered and is, in real-time, succumbing to the cascading pressures of e-commerce and Amazon. In the age of the internet, nobody needs a distribution middleman. Particularly at scale. The lost customer reflects that. Godspeed, PFS.”
Just saved like 1,382,222 words.
S&P further predicts a double-digit sales decline and negative free cash flow in 2018 and 2019, “with debt service and operating expenses funded largely with asset-backed loan (ABL) borrowings.” Slap a mid 5s multiple on this sucker and it looks like the first lien term loan holders will eventually be the owners of a shiny not-so-new pet food distributor! Dogs everywhere lament.

In the past 10 years, the share of U.S. adults living without a spouse or partner has climbed to 42%, up from 39% in 2007, when the Census Bureau began collecting detailed data on cohabitation.
Two important demographic trends have influenced this phenomenon. The share of adults who are married has fallen, while the share living with a romantic partner has grown. However, the increase in cohabitation has not been large enough to offset the decline in marriage, giving way to the rise in the number of “unpartnered” Americans.
Maybe the rise in co-habitation among romantic partners and the decline in marriage has something to do with the decline of importance of religion. Note this chart:

That said, the decline seems to have more to do with millennial attitudes towards religion AND the institution of marriage than anything else.
What does this have to do with any of you? Well, it seems that attitudes towards marriage are creating some retail distress. In June, Alfred Angelo filed for chapter 7 bankruptcy — much to the chagrin of countless brides-to-be who were left uncertain as to the delivery status of their ordered gowns. Take cover…insert peak Bridezilla.
David’s Bridal Inc. swooped in and tried to save the day. Because HOT DAMN retail is cold today. Customer acquisition needs to come from somewhere. And David’s Bridal needs all the help it can get.
The Conshohocken Pennyslvania-based retailer is the largest American bridal-store chain, specializing in wedding dresses, prom gowns, and other formal wear. The company has approximately 300 stores nationally (and declining). It also has approximately $1 billion of debt hanging over its balance sheet like an albatross. Upon information and belief (because the company is private), the capital structure includes a $125 million revolving credit facility, an approximately $500 million term loan due October 2019, and $270 million of unsecured notes due October 2020. The notes are trading at roughly half of par value, reflecting distress and a negative outlook on the possibility of full payment. Justifiably so. With EBITDA at roughly $19 million a quarter, the company appears 9.5x+ leveraged. And you thought YOUR wedding dress was expensive.
Why so much debt you ask? Well, c’mon now. Surely you’ve been reading us long enough to know the answer: private equity, of course. The company was taken private in a 2012 leveraged buyout by Clayton, Dubilier & Rice. (Petition Note: Callback to that Law360 article where private equity lawyers and bankers alleged that PE firms take too much flack…HAHAHA).
In light of recent trends and the debt, Moody’s recently downgraded David’s Bridal to “negative,” noting:
"‘In our view, this is a reflection of the intense competition in the sector and casualization of both gowns and bridesmaids dresses," Raya Sokolyanska, a Moody's analyst, wrote in a note to investors.”
Competition? You’ve got that right. H&M is all over this space too — grasping at straws to salvage its own languishing prospects.
Consequently, Reuters reported that the company is in talks with Evercore Group LLC ($EVR) to help it address its balance sheet. If hired, we think it would be hilarious if Evercore included this Marketwatch article entitled, “5 brides share their financial wedding regrets” in its pitch to lenders. Choice bit,
“Clare Redway, a marketing director based in Brooklyn who married in June 2016 said she wishes she spent more on the wedding dress, or at least found a more unique one. ‘I just got mine on sale at David’s Bridal,’ she said.”
That ought to stir up some concessions.
A few weeks back, we wrote this in “👞UGGs & E-Comm Trample Birkenstock👞,”
“Mere days away from a Nine West bankruptcy filing, we can’t help but to think about how quickly the retail landscape is changing and the impact of brands. Why? Presumably, Nine West will file, close the majority of - if not all of - its brick-and-mortar stores and transfer its brand IP to its creditors (or a new buyer). For whatever its brand is worth. We suppose the company’s lenders - likely to receive the company’s IP in a debt-for-equity swap, will soon find out. We suspect ‘not a hell of a whole lot’.”
Now we know: $123 million. (Frankly more than we expected.)
Consistent with the micro-brands discussion above, we also wrote,
“Saving the most relevant to Nine West for last,
Sales at U.S. shoe stores in February 2017 fell 5.2%, the biggest year-over-year tumble since 2009. Online-only players like Allbirds, Jack Erwin, and M.Gemi have gained nearly 15 percentage points of share over five years.
Yes, the very same Allbirds that is so popular that it is apparently creating wool shortages. Query whether this factor will be featured in Nine West’s First Day Declaration with such specificity. Likely not.”
Now we know this too: definitely not.
But Nine West Holdings Inc., the well-known footwear retailer, has, indeed, finally filed for bankruptcy. The company will sell the intellectual property and working capital behind its Nine West and Bandolino brands to Authentic Brands Group for approximately $200 million (inclusive of the above-stated $123 million allocation to IP, subject to adjustment) and reorganize around its One Jeanswear Group, The Jewelry Group, the Kasper Group, and Anne Klein business segments. The company has a restructuring support agreement (“RSA”) in hand with 78% of its secured term lenders and 89% of its unsecured term loan lenders to support this dual-process. The upshot of the RSA is that the holders of the $300 million unsecured term loan facility will own the equity in the reorganized entity focused on the above-stated four brands. The case will be funded by a $247.5 DIP ABL which will take out the prepetition facility and a $50mm new money dual-draw term loan funded by the commitment parties under the RSA (which helps justify the equity they’ll get).
Regarding the cause for filing, the company notes the following:
“The unprecedented systemic economic headwinds affecting many brick-and-mortar retailers (including certain of the Debtors’ largest customers) have significantly and adversely impacted the operating performance of the Debtors’ footwear and handbag businesses over the past four years. The Nine West Group (and, prior to its sale, Easy Spirit®), the more global business, faced strong headwinds as the macro retail environment in Asia, the Middle East, and South America became challenged. This was compounded by a difficult department store environment in the United States and the Debtors’ operation of their own unprofitable retail network. The Debtors also faced the specific challenge of addressing issues within their footwear and handbag business, including product quality problems, lack of fashion-forward products, and design missteps. Although the Debtors implemented changes to address these issues, and have shown significant progress over the past several years, the lengthy development cycle and the nature of the business did not allow the time for their operating performance within footwear and handbags to improve.”
Regarding the afore-mentioned “macro trends,” the company further highlights,
“…a general shift away from brick-and-mortar shopping, a shift in consumer demographics away from branded apparel, and changing fashion and style trends. Because a substantial portion of the Debtors’ profits derive from wholesale distribution, the Debtors have been hurt by the decline of many large retailers, such as Sears, Bon-Ton, and Macy’s, which have closed stores across the country and purchased less product for their stores due to decreased consumer traffic. In 2015 and 2016, the Debtors experienced a steep and unanticipated cut back on orders from two of the Debtors’ most significant footwear customers, which led to year over year decreases in revenue of $16 million and $46 million in 2015 and 2016, respectively. These troubles have been somewhat offset by e-commerce platforms such as Amazon and Zappos, but such platforms have not made up for the sales volume lost as a result of brick-and-mortar retail declines.”
No Allbirds mention. Oh well.
But wait! Is that a POSITIVE mention of Amazon ($AMZN) in a chapter 11 filing? We’re perplexed. Seriously, though, that paragraph demonstrates the ripple effect that is cascading throughout the retail industrial complex as we speak. And it’s frightening, actually.
On a positive note, The One Jeanswear Group, The Jewelry Group, the Kasper Group, and Anne Klein business segments, however, have been able to “combat the macro retail challenges” — just not enough to offset the negative operating performance of the other two segments. Hence the bifurcated course here: one part sale, one part reorganization.
But this is the other (cough: real) reason for bankruptcy:

Source: First Day Declaration
Soooooo, yes, don’t tell the gentlemen mentioned in the Law360 story but this is VERY MUCH another trite private equity story. 💤💤 With $1.6 billion of debt saddled on the company after Sycamore Partners Management LP took it private in 2014, the company simply couldn’t make due with its $1.6 billion in net revenue in 2017. Annual interest expense is $113.9 million compared to $88.1 million of adjusted EBITDA in fiscal year 2017. Riiiiight.
A few other observations:
Leases. The company is rejecting 75 leases, 72 of which were brick-and-mortar locations that have already been abandoned and turned over to landlords. Notably, Simon Property Group ($SPG) is the landlord for approximately 35 of those locations. But don’t sweat it: they’re doing just fine.
Liberal Definitions. As Interim CEO, the Alvarez & Marsal LLC Managing Director tasked with this assignment has given whole new meaning to the word “interim.” Per Dictionary.com, the word means “for, during, belonging to, or connected with an intervening period of time; temporary; provisional.” Well, he’s been on this assignment for three years — nearly two as the “interim” CEO. Not particularly “temporary” from our vantage point. P.S. What a hot mess.
Chinese Manufacturing. Putting aside China tariffs for a brief moment, if you're an aspiring shoe brand in search of manufacturing in China and don't know where to start you might want to take a look at the Chapter 11 petitions for both Payless Shoesource and Nine West. A total cheat sheet.
Chinese Manufacturing Part II. If President Trump really wants to flick off China, perhaps he should reconsider his (de minimus) carried interest restrictions and let US private equity firms continue to run rampant all over the shoe industry. If the recent track record is any indication, that will lead to significantly over-levered balance sheets borne out of leveraged buyouts, inevitable bankruptcy, and a top 50 creditor list chock full of Chinese manufacturing firms. Behind $1.6 billion of debt and with a mere $200 million of sale proceeds, there’s no shot in hell they’d see much recovery on their receivables and BOOM! Trade deficit minimized!!
Yield Baby Yield! (Credit Market Commentary). Sycamore’s $120 million equity infusion was $280 million less than the original binding equity commitment Sycamore made in late 2013. Why the reduction? Apparently investors were clamoring so hard for yield, that the company issued more debt to satisfy investor appetite rather than take a larger equity check. Something tells us this is a theme you’ll be reading a lot about in the next three years.
Athleisure & Casual Shoes. The fleeting athleisure trend took quite a bite out of Nine West’s revenue from 2014 to 2016 — $36 million, to be exact. Jeans, however, are apparently making a comeback. Meanwhile, the trend towards casual shoes and away from pumps and other Nine West specialties, also took a big bite out of revenue. Enter casual shoe brand, GREATS, which, like Allbirds, is now opening a store in New York City too. Out with the old, in with the new.
Sycamore Partners & Transparency in Bankruptcy. Callback to this effusive Wall Street Journal piece about the private equity firm: it was published just a few weeks ago. Reconcile it with this statement from the company, “After several years of declines in the Nine West Group business, part of the investment hypothesis behind the 2014 Transaction was that the Nine West® brand could be grown and strong earnings would result.” But “Nine West Group net sales have declined 36.9 percent since fiscal year 2015—from approximately $647.1 million to approximately $408 million in the most recent fiscal year.” This is where bankruptcy can be truly frustrating. In Payless Shoesource, there was considerable drama relating to dividend recapitalizations that the private equity sponsors — Golden Gate Capital Inc. and Blum Capital Advisors — benefited from prior to the company’s bankruptcy. The lawsuit and accompanying expert report against those shops, however, were filed under seal, keeping the public blind as to the tomfoolery that private equity shops undertake in pursuit of an “investment hypothesis.” Here, it appears that Sycamore gave up after two years of declining performance. In the company’s words, “Thus, by late 2016 the Debtors were at a crossroads: they could either make a substantial investment in the Nine West Group business in an effort to turn around declining sales or they could divest from the footwear and handbag business and focus on their historically strong, stable, and profitable business lines.” But don’t worry: of course Sycamore is covered by a proposed release of liability. Classic.
Authentic Brands Group. Authentic Brands Group, the prospective buyer of Nine West's IP in bankruptcy, is familiar with distressed brands; it is the proud owner of the Aeropostale and Fredericks of Hollywood brands, two prior bankrupt retailers. Authentic Brands Group is led by a the former CEO of Hilco Consumer Capital Corp and is owned by Leonard Green & Partners. The proposed transaction means that Nine West's brand would be transferred from one private equity firm to another. Kirkland & Ellis LLP represented and defended Sycamore Partners in the Aeropostale case as Weil Gotshal & Manges LLP & the company tried to go after the private equity firm for equitable subordination, among other causes of action. Kirkland prevailed. Leonard Green & Partners portfolio includes David's Bridal, J.Crew, Tourneau and Signet Jewelers (which has an absolutely brutal 1-year chart). On the flip side, it also owns (or owned) a piece of Shake Shack, Soulcycle, and BJ's. The point being that the influence of the private equity firm is pervasive. Not a bad thing. Just saying. Today, more than ever, it seems people should know whose pockets their money is going in to.
Official Committee of Unsecured Creditors. It’ll be busy going after Sycamore for the 2014 spin-off of Stuart Weitzman®, Kurt Geiger®, and the Jones Apparel Group (which included both the Jones New York® and Kasper® brands) to an affiliated entity for $600 million in cash. Query whether, aside from this transaction, Sycamore also took out management fees and/or dividends more than the initial $120 million equity contribution it made at the time of the transaction. Query, also, whether Weil Gotshal & Manges LLP will be pitching the committee to try and take a second bite at the apple. See #8 above. 🤔🤔
Timing. The company is proposing to have this case out of bankruptcy in five months.
This will be a fun five months.
Let’s start with this SHAMELESS Law360 piece (paywall) which doubles as a promotional puff piece on behalf of the private equity industry. Therein a number of conflicted professionals go on record to say that private equity has taken far too much flack for the demise of retail. The piece is pure comedy…
To read the rest of this a$$-kicking commentary, you need to be a Member.
This week William Cohan and Vanity Fair released a once-in-fifteen-years piece with the infamous Sears Holding ($SHLD) investor, Eddie Lampert. It’s a whopper and worth a read.
The mess that is Sears is quantified here:
“But today those triumphs are largely obscured by his worst mistake: the 2005 merging of Sears, the iconic retailer whose doorstop mail-order catalogue was once a fixture in nearly every American home, with the downmarket Kmart chain, which he had brought out of bankruptcy in 2003. Twelve years on, this blundering into retail has made him a poster boy for what some people think is wrong with Wall Street and, in particular, hedge funds. Under his management the number of Sears and Kmart stores nationwide has shrunk to 1,207 from 5,670 at its peak, in the 2000s, and at least 200,000 Sears and Kmart employees have been thrown out of work. The pension fund, for retired Sears employees, is underfunded by around $1.6 billion, and both Lampert and Sears are being sued for investing employees’ retirement money in Sears stock, when the top brass allegedly knew it was a terrible investment.”
To put this in perspective, people are in an uproar about the liquidation of Toys R Us which has 33,000 employees. Sears, while still in business, has had attrition of 6x that. But wait. That’s just on the human capital side. What about the actual capital side:
“In 2013, Lampert, who was chairman of the board, had himself named C.E.O. of Sears Holdings, as the combined company is known. He’s had a rough four years since then. The company has suffered some $10.4 billion in losses and a revenue decline of 47 percent, to $22 billion.”
And on the financial side:
“…Sears Holdings stock price has slumped to $2 a share, down considerably from the high of $134 per share some 11 years ago. Sears Holdings now has a market value of around $250 million, making Lampert’s nearly 60 percent stake worth $150 million.”
How. The. Eff. Is. This. Business. Still. Alive. Well, this:
“The vultures are circling, waiting for Lampert to throw in the towel so they can try to make money by buying Sears’s discounted debt. But Lampert continues to claim that’s not going to happen if he can help it.”
Gotta give the guy credit for perseverance.
For those who may be too young or too weathered to remember, KMart was actually a successful turnaround for the first few years after Lampert converted his (acquired) debt position into equity. Operating profit was $1.3 billion in 2004 and 2005. But then he decided to combine KMart and Sears. Thereafter, the big issues began.
Interestingly, the piece suggests that Lampert was “ahead of his time” by de-emphasizing investment in the in-store experience and focusing on e-commerce. But shoppers didn’t buy online. Cohan writes,
“At the time they were just not comfortable enough with the technology to do so. Whatever the reason, Sears’s Web site never remotely rivaled the sales in the stores. Or on Amazon.”
Maybe because, even today, the website is a cluttered mess that will give even those with the most robust heart arrhythmia. In that respect, the online experience mirrors the offline experience. And this runs afoul of current theories of retail. Jeremy Liew of Litespeed Venture Partners writes about new “omnichannel” retailers like Bonobos, Allbirds, Away, Modcloth and Glossier and the new “customer acquisition channel”:
“All retailers need to be wherever their customers are. And for all retailers, their best customers are in every channel. This is just as true for DNVBs. For Bonobos for example, customers who buy first in store spend 2x more and have half the return rate. But more importantly, they spend 30% more online over the next 12 months.
But these DNVBs think about physical retail in a very different way than incumbent retailers. They are not measured purely on “four wall profitability” or $/sq foot, some of the traditional metrics in retail. Many of the stores are showrooms, they don’t carry full inventory. Most support iPads or other ways to browse the online catalogue.
These brands understand the importance of experiential marketing, and they see their physical spaces as a platform to engage deeply with their customers. In short, they see physical retail as customer acquisition channels for their online business. In some cases, a contribution positive customer acquisition channel. In others, a customer acquisition channel whose costs you can compare to Facebook, Instagram, Google or other customer acquisition channels. But always the online business grows.”
For this to work, Everlane’s Michael Preysman says you “must make it look good.” If only Lampert bought in to this premise. Instead, Sears’ online experience mirrors the offline experience: horrible user experience + dilapidated stores = a wholesale contravention of, as Liew points out, everything that successful retailers are doing today. It’s the customer rejection channel. Hence the suspicions from outsiders — which Lampert vehemently denies — that he’s treating Sears like a private company, milking the company for his own benefit, and slowly liquidating it to the point of bankruptcy. Once in bankruptcy, Lampert will allegedly be able to leverage his place in the capital structure to own the company on the backend. It would be a leaner version of Sears — free of debt, onerous leases and pension obligations. Why invest in customer or employee experience now if this is a possibility later? Good question.