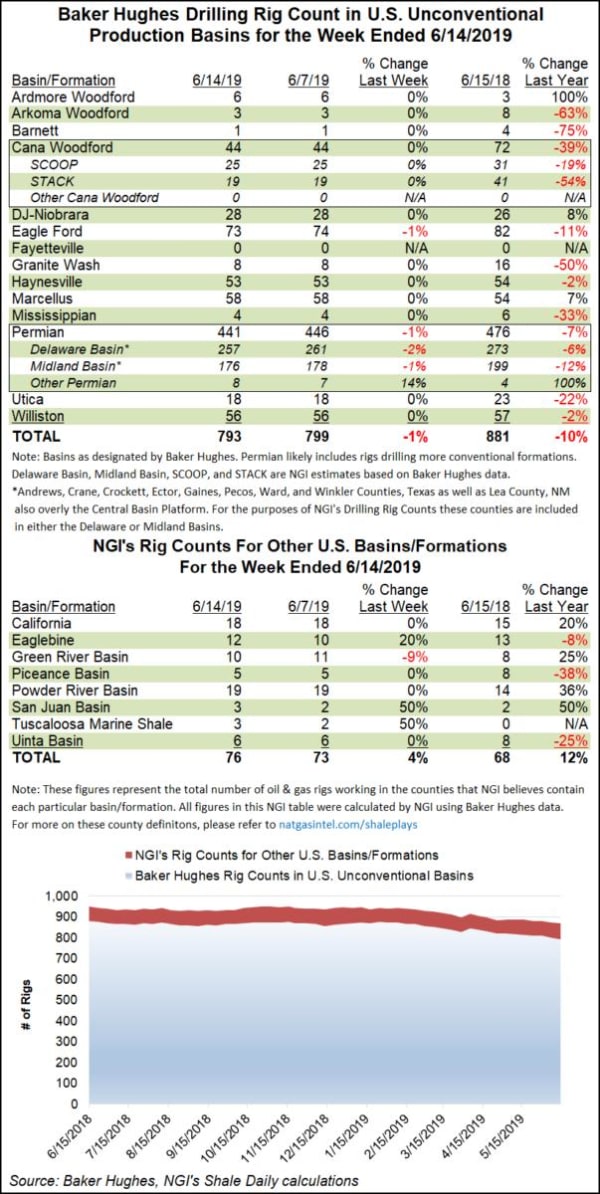
💩There’s No End in Sight for Retail Pain (Long the “Playbook”)💩
Retail, retail, retail.
Brutal. Absolutely B.R.U.T.A.L.
Avenue Stores LLC, a speciality women’s plus-size retailer with approximately 2,000 employees across its NJ-based HQ* and 255 leased stores,** is the latest retailer to find its way into bankruptcy court. On Friday, August 16, Avenue Stores LLC filed for chapter 11 bankruptcy in the District of Delaware. Like Dressbarn, another plus-size apparel retailer that’s in the midst of going the way of the dodo, any future iteration of the Avenue “brand” will likely exist only on the interwebs: the company intends to shutter its brick-and-mortar footprint.
What is Avenue? In addition to a select assortment of national brands, Avenue is a seller of (i) mostly “Avenue” private label apparel, (ii) intimates/swimwear and other wares under the “Loralette” brand and (iii) wide-width shoes under the “Cloudwalkers” brand. The company conducts e-commerce via “Avenue.com” and “Loralette.com.” All of this “IP” is the crux of the bankruptcy. More on this below.
But, first, a digression: when we featured Versa Capital Management LP’s Gregory Segall in a Notice of Appearance segment back in April, we paid short shrift to the challenges of retail. We hadn’t had an investor make an NOA before and so we focused more broadly on the middle market and investing rather than Versa’s foray into retail and its ownership of Avenue Stores LLC. Nevertheless, with the benefit of 20/20 hindsight, we can now see some foreshadowing baked into Mr. Siegel’s answers — in particular, his focus on Avenue’s e-commerce business and the strategic downsizing of the brick-and-mortar footprint. Like many failed retail enterprises before it, the future — both near and long-term — of Avenue Stores is marked by these categorical distinctions. Store sales are approximately 64% of sales with e-commerce at approximately 36% (notably, he cited 33% at the time of the NOA).
A brand founded in 1987, Avenue has had an up-and-down history. It was spun off out of Limited Brands Inc. and renamed in 1989; it IPO’d in 1992; it was then taken private in 2007. Shortly thereafter, it struggled and filed for bankruptcy in early 2012 and sold as a going-concern to an acquisition entity, Avenue Stores LLC (under a prior name), for “about $32 million.” The sale closed after all of two months in bankruptcy. The holding company that owns 100% of the membership interests in Avenue Stores LLC, the operating company, is 99%-owned by Versa Capital Management.
Performance for the business has been bad, though the net loss isn’t off the charts like we’ve seen with other recent debtors in chapter 11 cases (or IPO candidates filing S-1s, for that matter). Indeed, the company had negative EBITDA of $886k for the first five months of 2019 on $75.3mm in sales. Nevertheless, the loss was enough for purposes of the debtors’ capital structure. The debtors are party to an asset-backed loan (“ABL”) memorialized by a credit agreement with PNC Bank NA, a lender that, lately, hasn’t been known for suffering fools. The loan is for $45mm with a $6mm first-in-last-out tranche and has a first lien on most of the debtors’ collateral.
The thing about ABLs is that availability thereunder is subject to what’s called a “borrowing base.” A borrowing base determines how much availability there is out of the overall credit facility. Said another way, the debtors may not always have access to the full facility and therefore can’t just borrow $45mm willy-nilly; they have to comply with certain periodic tests. For instance, the value of the debtors’ inventory and receivables, among other things, must be at a certain level for availability to remain. If the value doesn’t hold up, the banks can close the spigot. If you’re a business with poor sales, slim margins, diminishing asset quality (i.e., apparel inventory), and high cash burn, you’re generally not in very good shape when it comes to these tests. With specs like those, your liquidity is probably already tight. A tightened borrowing base will merely exacerbate the problem.
TIRED OF GETTING ONLY PART OF THE STORY? US TOO! CLICK HERE AND SUBSCRIBE TO GET UNLIMITED ACCESS TO OUR PREMIUM CONTENT! (YOU WON’T REGRET IT)